Now that 2024 is behind us, it’s time to look ahead to 2025, a year full of exciting fintech industry trends that are set to transform everything we know about money. The rapid adoption of contemporary fintech growth trends is already making a significant impact. The global fintech market is projected to grow from USD 25.18 billion in 2024 to USD 644.6 billion by 2029. While AI has played a major role in fintech, it’s no longer the most groundbreaking trend. Innovations such as Banking-as-a-Platform, embedded finance, and green fintech initiatives are now taking center stage. Dive deeper into these trends and more in our latest article.

Embedded finance: Seamless financial services everywhere
Embedded finance is one of the most prominent fintech trends for 2025. It enables businesses, both in the financial and non-financial sectors, to expand their customer base and enhance client engagement. Essentially, embedded finance integrates financial services into non-financial offerings, helping companies meet their customers where they are. This can include providing loans, “Buy Now, Pay Later” options, and other payment solutions.
While embedded finance isn’t a new concept, it has gained significant traction in recent years. E-commerce companies, in particular, are now offering financial services directly on their websites, reducing the need for clients to be referred to banks or other financial institutions. This trend is rapidly growing online, reshaping the way consumers interact with financial services.
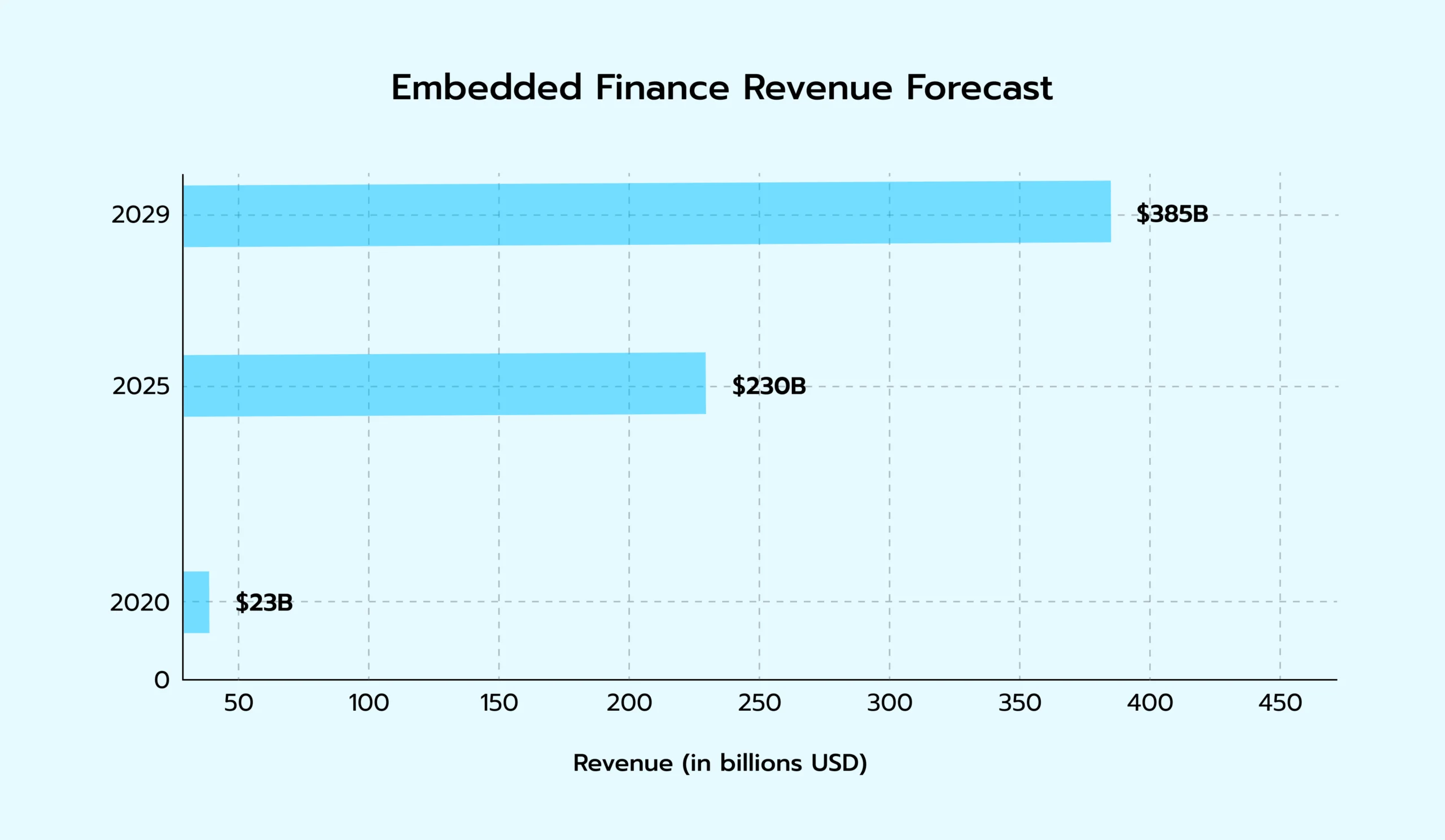
Chart 1: Embedded finance revenue forecast (2020-2029)
Source: KBV Research.
The latest data forecasts that the global embedded finance industry will expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.0%, reaching $384.8 billion by 2029. This growth reflects the clear benefits of investing in this technology. For customers, the convenience of paying for goods directly on an e-commerce website—without having to complete the purchase through a third-party site—makes the process easier and faster.
Businesses also stand to gain significantly from embedded finance. By offering embedded payments, companies gain access to a broader range of data analytics. They can process and store transaction data, which can then be analyzed to uncover patterns in customer behavior and purchasing trends. This valuable information can help influence decision-making and product planning, ultimately enhancing customer loyalty and providing a competitive edge in the marketplace.

The Amazonization of finance: Redefining customer expectations
Amazon’s revolutionary impact on the retail industry, which radically changed consumer expectations, gave rise to “Amazonization.” It has spread to the financial services industry, where customer-focused platforms that serve as a one-stop shop for various goods and services are attracting interest. The financial industry is following Amazon’s lead, which transformed purchasing by offering individualized experiences, aggressive prices, and social evidence through reviews.
Amazonization empowers the customer by creating seamless systems that allow users to search for, evaluate, and purchase financial products tailored to their needs. These platforms, driven by data and transparency, provide real-time ratings, user reviews, KPIs, and value-for-money insights. This shift not only caters to the tech-savvy Generation Y, currently the largest consumer group, but also ensures that financial institutions stay competitive in a world that is becoming increasingly digital.
With PSD2 and associated regulations supporting them, European banks are implementing this strategy as product aggregators, emphasizing transparency and choice to give their customers the most value. They have a competitive advantage since they provide cutting-edge financial solutions via platforms that smoothly combine third-party and proprietary services. It goes without saying that tech giants like Google, Apple, and Amazon will upend the financial services industry by establishing online marketplaces for banking goods.
The message is clear: it’s either adapt or get left behind. The moment has come to take action, whether through exclusive and distinctive services or complete digital makeovers into stand-alone platforms. In this customer-centric age, the financial sector sells more than simply services; it sells value, trust, and smooth experiences.

Bank as a platform (BaaP): A new era of collaboration
Financial institutions’ conventional methods of operation and innovation have evolved with the concept of Bank-as-a-Platform (BaaP). By utilizing their reliable infrastructure, banks can now collaborate directly with external providers, enabling them to do more than just sell goods and services to consumers. Instead, they can create an open innovation hub that opens up new revenue streams and enhances customer engagement.
Unlike Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS), where third parties integrate banking capabilities into their platforms, BaaP operates through APIs that integrate third-party services into the bank’s ecosystem. Under this model, the bank becomes the client’s main point of contact, while benefiting from a wider range of digital services provided by its partners.
Among BaaP’s prominent features are:
- Cloud hosting for flexibility and scalability.
- Open architectures to enable smooth integration.
- Ensuring cost-effectiveness by charging only for usage.
In contrast to BaaS, BaaP enables banks to increase their offers while keeping direct control over client connections by integrating third-party services into their own ecosystem. This keeps them at the heart of customer experience.
|
Banking as a Platform (BaaP) |
Banking as a Service (BaaS) |
| Definition |
Banks integrate third-party services into their ecosystem. |
Third-party platforms integrate banking services via APIs. |
| Primary User |
Banks leverage third-party services. |
Businesses embed banking services into their products. |
| Core Focus |
Open innovation and expanding service offerings. |
Enabling non-banking businesses to offer financial services. |
| Customer Ownership |
The bank retains the customer relationship. |
Third-party businesses own the customer relationship. |
| Infrastructure |
Built on open architectures and cloud hosting. |
Delivered as an API-driven service by the bank. |
| Revenue Streams |
New revenue from third-party partnerships and services. |
Licensing fees and transactional revenue from APIs. |
| Flexibility |
Rapid service deployment using partner APIs. |
Facilitates embedded finance for third parties. |

Edge AI integration: Real-time intelligence at the edge
Whether it’s a wearable, smartphone, or Internet of Things device, edge AI is pushing the limits of real-time data processing by putting computing power closer to the source. Unlike conventional cloud-based models, edge AI eliminates latency, enabling immediate decision-making for critical applications such as fraud detection and personalized financial advising. For instance, if someone attempts an unusual transaction on your account or makes a large purchase abroad, edge AI will instantly detect and flag it as suspicious. Simultaneously, it can block the transaction in real-time, without sending data to a central server.
Edge AI not only improves performance but also enhances privacy. By processing data locally, it minimizes the potential for security risks, as there’s no need for significant data transmission. This shift to edge computing is a natural progression for the fintech industry, which increasingly demands hyper-personalization, security, and real-time processing. Fintech companies should see it as a strategic necessity in today’s fast-paced, data-driven economy rather than a passing trend.

Cybersecurity and fraud prevention: The backbone of trust
Using specialized, cutting-edge frameworks can help cybersecurity in the financial industry keep ahead of changing threats. Financial institutions are concentrating on enhancing transparency and guaranteeing adherence to new regulatory standards for data security and client safety as PSD3 preparations heat up.
One important way to mitigate the vulnerabilities caused by weak or stolen passwords is to use passwordless authentication. Techniques like magic links and secure device-based authentication allow consumers to access their data easily and securely. Additionally, behavioral authentication adds another layer of protection by analyzing patterns such as typing speed, navigation habits, and device usage to detect suspicious activities.
Because access is linked to distinct physical traits, biometric technologies—such as voice verification, facial recognition, and fingerprint scanning—provide an additional degree of trust. When combined with traditional security measures, these biometrics create a multi-layered defense system that stops scammers in their tracks, while ensuring a seamless and secure experience for users.

Cooling crypto: Consumers return to traditional investing
With six out of ten customers questioning whether cryptocurrencies are a wise investment in the current economic environment, interest in them is fading. The extreme volatility of cryptocurrencies, unclear regulations, and the recent failures of major platforms are the main causes of this sentiment cooling. As a result, a lot of investors are turning back to more conventional options like stocks, bonds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), which are well-regulated, stable, and have predictable returns.
However, some investors continue to benefit from cryptocurrency due to its low entry barrier and ongoing advancements. Institutional players continue to concentrate on the underlying blockchain technology for long-term applications, while the average investor prefers more conventional approaches.
While interest in cryptocurrency may have cooled, it is still relevant today. Conventional investing may be reigning supreme at the moment, but cryptocurrency remains a niche player with the potential to rise again, especially if favorable fintech market conditions reemerge.

Green FinTech: Driving sustainable finance through innovation
Green FinTech uses technology to promote profitable and significant financial activities while encouraging environmental stewardship. It is essential for resolving climate-related issues and guaranteeing sustained global resilience.
The following are some of the fundamental components of Green FinTech that propel such revolutionary change:
- Natural Capital Accounting: By assigning a monetary value to natural resources, this approach helps companies better monitor and control their environmental impact.
- Climate Risk Assessment: Businesses can make more resilient decisions in a volatile environment by using predictive analytics to evaluate the potential financial risks associated with climate change.
- Carbon Offsetting: Investing in renewable energy, forestry, and carbon capture projects to neutralize carbon emissions is known as carbon offsetting.
- ESG Data Intelligence and Reporting: Provides transparency for stakeholders by enabling firms to monitor and report on environmental, social, and governance parameters.
- Sustainable Banking: To support environmental initiatives, sustainable banking offers eco-friendly financial products, green loans, and funding for renewable energy projects.
- Climate Crypto: Uses blockchain technology to manage transparent carbon credit trades and finance environmental initiatives.
- Impact Investing: The practice of allocating funds to projects that generate measurable social and environmental benefits, alongside financial returns.
Green FinTech aims to create a financial system focused on responsibility, innovation, and environmental health. It is far more than just about sustainability.

The rise of financial super apps: One app to rule them all
A mobile platform that combines a variety of financial services, including banking, payments, investing, insurance, and much more, into a single, seamless environment is known as a financial super app. The key benefit of these digital assets is convenience: people can handle all aspects of their financial lives while on the go. Many super apps offer services like online shopping, entertainment, and even cost tracking in addition to account administration and mobile payments.
WeChat, introduced by Tencent in 2011, is one of the most well-known super apps on the market. Originally a chat app, it evolved into a mega app offering over a million micro-applications and services, from games and ticket booking to loans and financial transactions. With over 800 million monthly active users, WeChat exemplifies how a cohesive ecosystem can transform consumer behavior. The ability to leverage big data and advanced technologies like artificial intelligence to create highly personalized experiences is what makes super apps one of the most important fintech trends.
The road ahead for FinTech in 2025
The financial services and technology industry doesn’t reward those organizations that cling to traditional banking. It rewards finance leaders who are brave enough to automate their processes, embrace industry trends, and stay on top of the market by providing agile customer solutions for personal finance. In the famous words of Arthur C. Clarke, “Any sufficiently advanced technology is equivalent to magic.” Businesses in the fintech sector have the chance to embrace this magic and become contemporary magicians. For those who haven’t made the initial moves, now’s the moment to get started.
Want to learn more about the fintech ecosystem’s current trends? Contact Avenga, your trusted partner in the fintech landscape.



















