End of Support for Microsoft Products: What You Need to Know
Stay informed about the end of support for Microsoft Office 2016 & 2019, Exchange Server 2016 & 2019, and Windows 10.
We all have heard a lot about marketing, trends, campaigns and other things which should be used in fast growing companies. In order to have an effective and profit-oriented marketing policy, we need to know who our customers are and be able to analyze their behavior. Market segmentation is a core marketing technique that can help us accomplish precisely that.
In this article I would like to give a short review of the importance of market segmentation and the different types of segmentation as well as their impact on marketing process.
My main goal is to demonstrate how you can achieve your strategic marketing goals with the help of modern segmentation approaches and powerful tools Marketing Cloud contains.
In order to make any business successful and profitable, we must put in a lot of effort and time, and of course financially invest in it. It requires that we carry out marketing campaigns and promotions as well. Ofcourse, we want to know if our campaigns provide the expected and effective results.
Each marketer realizes that during a marketing campaign there will be mixed results due to different customers’ behaviors, even with the best strategy used; and this is normal. We shouldn’t think that it is going badly and make hasty conclusions, or radically change the approach and/or strategy. We need to learn how to analyze the gathered information and to conduct future campaigns based on the derived results.
Suppose we have a customer base and we would like to send a message regarding a new autumn sales campaign for sportswear. Some of the customers were not interested in these types of messages and preferred not to receive them.
So, if we use our customer base for all mailings, we risk getting negative results: they may unsubscribe from the mailing list and even block our domain. The end result will be negative consequences for our business. What do we need to do? The answer is simple: we should use the oldest marketing trick – segmentation.
What is customer segmentation? Segmentation is an aggregating of prospective buyers into groups or segments with common needs, and who respond similarly to a marketing action. That means you have to divide the marketplace into parts, or segments, which are definable, actionable, profitable, and have a growth potential. With customer segmentation, we can personalize our marketing messages for better communication with the different groups of customers.
I would like to briefly describe different types of segmentation. This will help us in understanding which type we should use during Marketing Cloud campaigns and flows.
The most popular market segmentation types include:
This is one of the simplest and most frequently used forms of segmentation. This type of segmentation divides a population based on variables such as age, gender, family size, income, occupation, religion, race and/or nationality, etc.
This type of market segmentation divides the population on the basis of their behavior. Consumer behavior defines the way the general population responds to, uses or knows about a product, and their usage and decision-making patterns. The main goal is to understand your customer’s needs and desires according to their buying behavior.
For example, restaurants with a place to play for children, malls that use discounts card systems, holiday sales, etc.
This one uses the lifestyle of people, their social standing, activities, interests as well as their opinions. This type of segmentation is used to define a customer’s psychographic profile. It can tell a marketer about consumers’ preferences, their interests and their way of thinking. A person’s work processes or hobbies tell a lot about that individual.
For example, if a customer likes reading Agatha Christie’s books he/she may want to buy books about Agent 007 or Jason Bourne.
The name of this segmentation speaks for itself; it is based on geography. Customers have different needs according to their location.
For example, in hot countries a company can offer air conditioners, while in colder countries they might advertise and sell more heaters.
This segmentation groups customers depending on who decides to purchase a product within the company structure.
What does this mean for a business? Segmentation is an effective method that puts a focus of a company on the right market segments, which helps to increase competitiveness. Customer retention can be encouraged through the life cycle of a customer by better communication with them. A dialogue is hardly possible without knowing your target market. When we use a geographic segmentation, the company’s strategy can be immediately expanded to a nearby territory.
We’ve heard the phrase “strike while the iron’s hot’ meaning to take advantage of a window of opportunity when it opens. With segmented data from our customers’ purchasing behaviors, we’ll know exactly when these windows open and we will be able to capitalize on that perfect opportunity to make a sale.
That was the theory.
Now that we know what segmentation is and what it needs, it’s time to apply our knowledge in practice.
As you know, data in a Marketing Cloud can be organized in two ways: lists or data extensions. We can use them in a data model, for sending relevant and personalized content.
There is no need to deeply plunge into the definition of or the differences between these extensions and discuss all the details, but I will briefly highlight them in the table below:
| List-Based Data Model | Data Extension-Based Data Model |
| Lists contain 500,000 subscribers or less long term | Subscribers count is going to be greater than 500,000 |
| If you prefer simplicity over performance | If data model supports multiple subscriber data sets, with separate definitions |
| If you do not require fast import speed | If you require fast import speeds |
| If you will use a limited number of subscriber attributes | If you send global messages |
| If you use the XML API | If you implement triggered sends |
| If you prefer a flexible subscription model | |
| If you use the SOAP or REST APIs |
NOTE: Be careful with selecting a data model. Review your current and future needs, and analyze all the requirements in order to compare the simplicity of implementation with the resulting performance.
If we use a List-Based Data Model we can do segmentation using Groups; Groups based on lists. This is a sublist of subscribers which we’ve taken from an appropriated list.
There are 2 types of Groups: filtered and random. We are interested in filtered ones.
NOTE: We can filter groups only by profile and preference attributes.
Profile attributes contain information regarding the subscriber (name, location, gender, age).
Preference attributes contain information about the subscribers’ preferences (type of communications, event types, new products, etc).
Also, Marketing Cloud provides a list of predefined measures which can be used in filters. For example: “_Total Transactional Sends Last 30 Days” or “_Total Unsubscribes for Marketing Sends Last 30 Days”. All these measures are based on system data views.
Let’s create a simple example. Suppose we have a list which contains our subscribers (“Europe Subscribers”). Our branch in Barcelona launches a sportswear promotion and offers a 40% discount for active young people who have a club card and prefer to receive messages by email. We want to create a mailing group (segment) for subscribers according to the example above.
In Email Studio under Subscribers select Groups and click Create. We should specify the type for our new group (in our case it’s a “Filtered Group”) and select source list (“Europe Subscribers”).
A Marketing Cloud provides a simple drag-and-drop interface to create a filter:
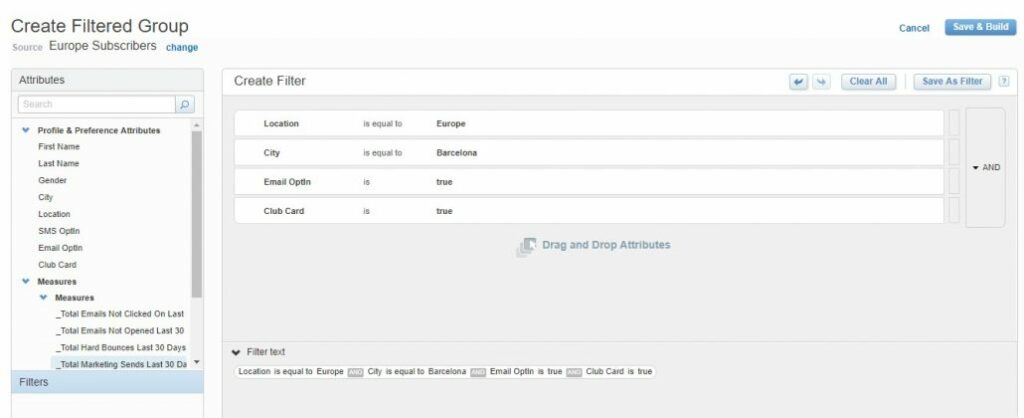
As a result we will have a mailing group for the appropriate segment of subscribers. Also, we saved time with the easy-to-use interface, however, we are restricted by subscriber attributes.
Data filter is a separate Marketing Cloud object which contains a group of criteria. We can use data filters as complex rules for segmentation lists or data extensions.
If we associate a Data filter with a list, it will result in an already known Group ; in the case of Data extensions we will get Filtered Data extensions. For creating a Data filter we use the same easy drag-and-drop interface as during a Group. A Data filter can be created and saved without applying it to any list or data extension; and we can reuse this filter definition with many lists or data extensions. This is very useful if you need to apply the same rules in different cases.
NOTE: We can’t associate a Data filter based on Profile attributes with a Data extension and vice versa.
To create a Data filter definition in Email Studio, under Subscriber, select the “Data Filters” menu item.
Using previous examples, we can create a separate Data filter with the following rules: City equals “Barcelona”, Location equals “Europe” and Email OptIn equals “True” and afterwards we can use it several times to create appropriate groups.
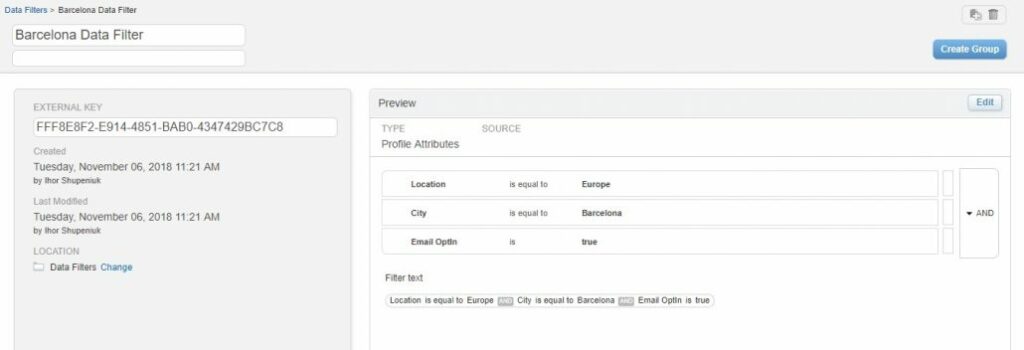
There is one more useful thing provided by a Marketing Cloud. As you already noticed I didn’t add as a last condition – “Club Card” equals True into the new data filter. This is because we created a general filter (as we did in the example above) and while creating a group or filtered data extension, we extended our filter with new necessary conditions and defined a more specific set of subscribers.
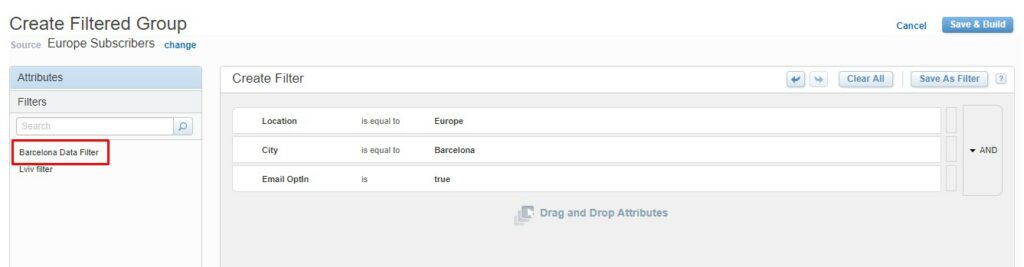
For example, in our case, we would like to add one more condition: “City” equals “Barcelona” or “Madrid”:
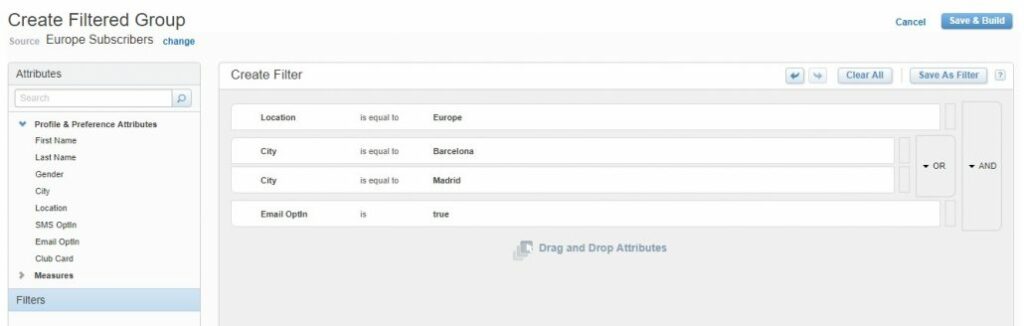
As was mentioned above, we have an opportunity to apply filtering fields, already created filters, and measures to data extensions. In the results, we will have a resulting data extension which takes the same characteristics as the source data extension: fields, data types and send options.
To create a Filtered data extension we should specify the method by which the data extension will be built as a “Filtered Data Extension”, select source data extension and then create an appropriate filter using the already known interface:
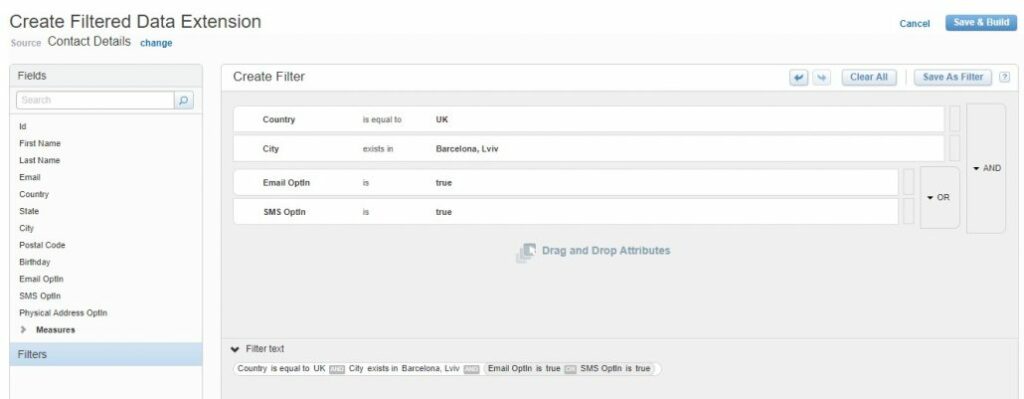
Newly added or modified records in a source data extension are not automatically added to filtered data extensions. And, if those records have field values eligible for our filter, we need to refresh the filtered data extension. So we can select the checkbox next to the filtered data extension to refresh it.
Now, a few words regarding automation with data filters. If we want to use an Automation studio for automated and periodical updating filtered lists (groups) or data extensions, we can create a Filter Activity. This activity will be based on a previously created data filter, which should exist before we can select it. Also, we should provide a name for the group or data extension to contain the resulting segment. Filter activities provide a more robust API support than groups.
In recent years an API provided to us by Salesforce, has been greatly improved and the documentation has become more structured and fuller. Everything that we do in an application interface can be implemented through the API.
For example, we can create an automation flow for getting the appropriate data from the list or data extension, and further updating the created segment. Automation will execute a scheduled Filter activity and will provide us with an up-to-date segment of contacts. To do this through the API, it should be implemented as outlined in these steps:
A Marketing Cloud API provides us with a lot of opportunities for customization and integration with other platforms.
If we use Data model based on Data extensions, Marketing Cloud provides us with one more segmentation method – Query activities.
This type of activity uses SQL to retrieve information from data extensions or system data views, which match our criteria, and then store result data in a data extension.
Suppose we have several data extensions which contain detailed information regarding contacts. We need to select only the records that meet certain criteria (those criteria rules can be based on field values from the different data extensions) and accumulate the necessary information in one data extension. As a result we will have a ready segment with detailed information, which can be used for personalization of our messages or landing pages. This is very convenient, isn’t it?
Query Activity is based on SQL Server 2005 capabilities. Unfortunately it has some restrictions: for example Temporary Tables, Common Table Expressions, User Defined Functions and Text or Image Functions are not supported.
Except some restrictions related to the SQL version, when working with SQL in a Marketing Cloud we need to remember a few important points:
To create a new Query activity in Automation Studio under the Activities menu item, we need to select SQL QUERY and click the “Create Activity” button. Then we should set the name, external key, and description to describe the activity within the application interface or API calls:
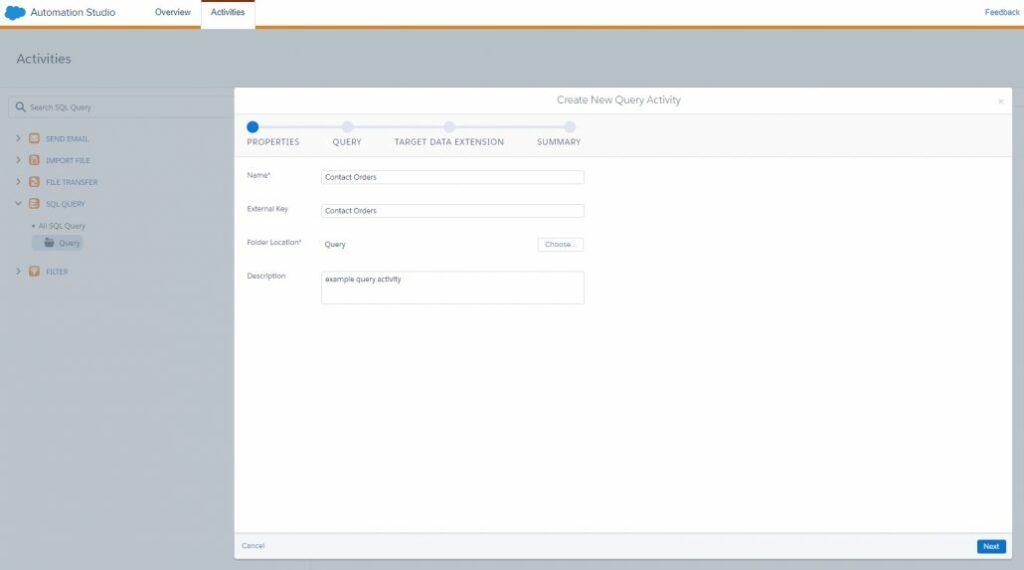
Then in the second step, we will directly generate the body of the SQL query. We can drag or double-click a column or an entire data extension name (if we want to add all fields from the data extension) to add it to the syntax. Also a query activity interface provides a validation tool to check the syntax of your SQL – just click the “Validate Syntax” button:
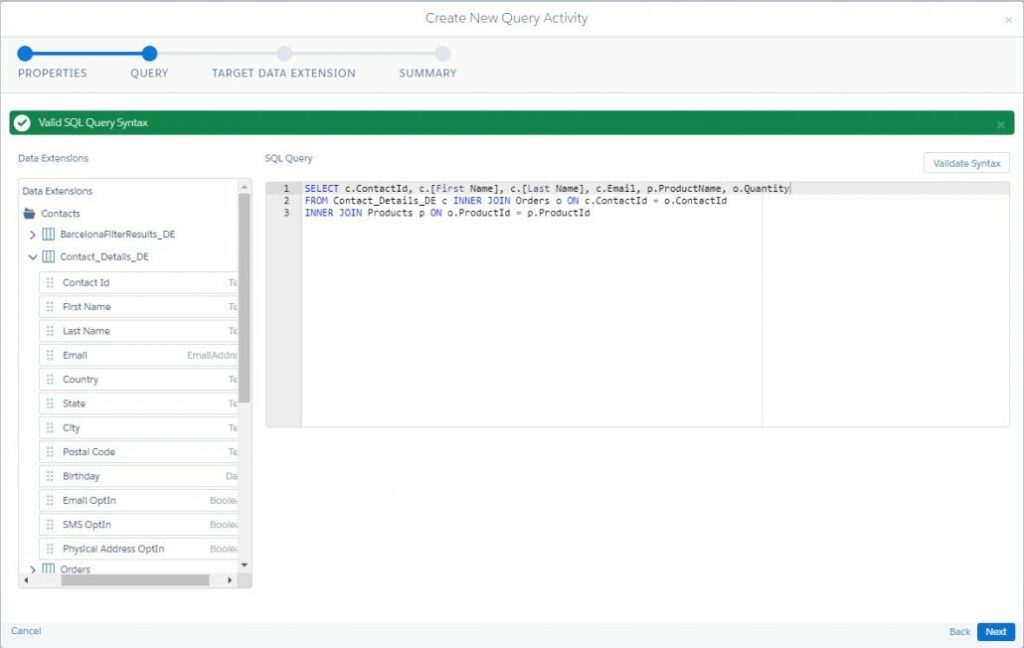
NOTE: To use a SQL query data extension from the parent business unit, we should add the prefix ENT. to the data extension name.
In the third step, we need to choose the target data extension that will store the query results. It should have been previously created.
NOTE: Fields and their data types in the target data extension must match the selected fields in the SQL query.
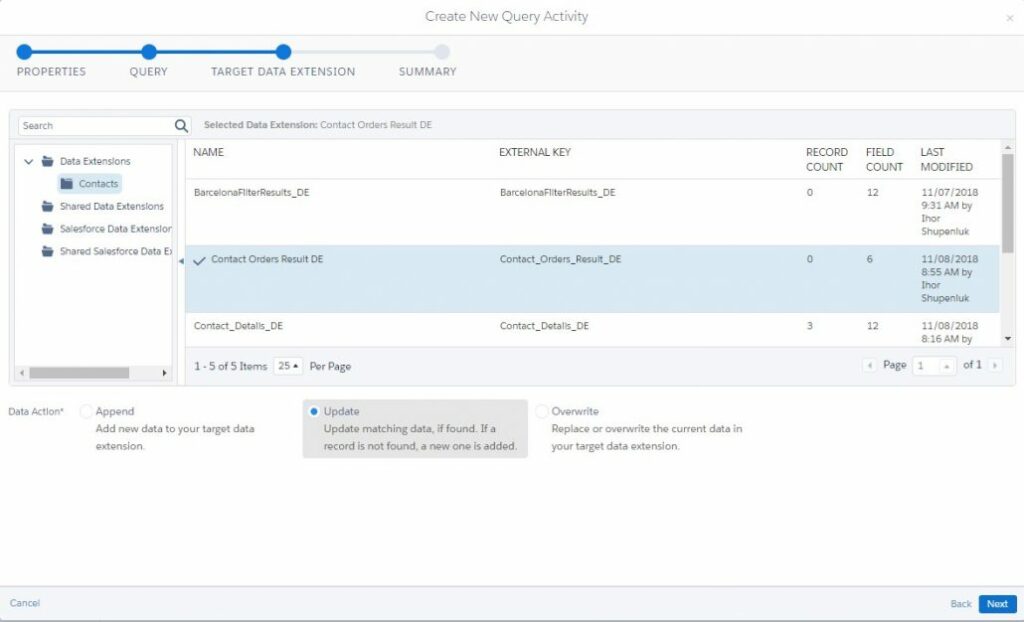
In this step we should do one more very important thing – choose the data action which the query activity will perform with data: append, update or override.
| Append | Adds a row in the target data extension for each row returned by the SQL query. All existing rows in the target will not be updated |
| Update | Updates values in the target data extension if field name matches field returned by SQL Query for rows whose Primary Key the SQL query returns. Rows returned by Query whose Primary Key does not exist in the target will be appended |
| Overwrite | Removes all existing rows in the target data extension and adds all new rows from the result of SQL Query |
NOTE: An executed SQL Query can take up to 30 minutes.
Just create a Query activity that can be executed immediately (open created activity and click the “Run” button), or as in the case with a Filter activity, a new scheduled Automation can be created, which will execute the current activity by scheduler.
As I mentioned, Query activities can work with system data views. Data views are Marketing Cloud system tables that store tracking information (data regarding sent emails, opened and bounced emails, subscribers, jobs, journeys, etc.). Query activities allow us to join Data views with each other or with Data extensions, and save the results in a target Data extension, as an already finished segment.
For example: create a segment that will contain all the subscribers who were sent a letter from a particular journey (‘Test Journey’) and who clicked the link inside this letter.
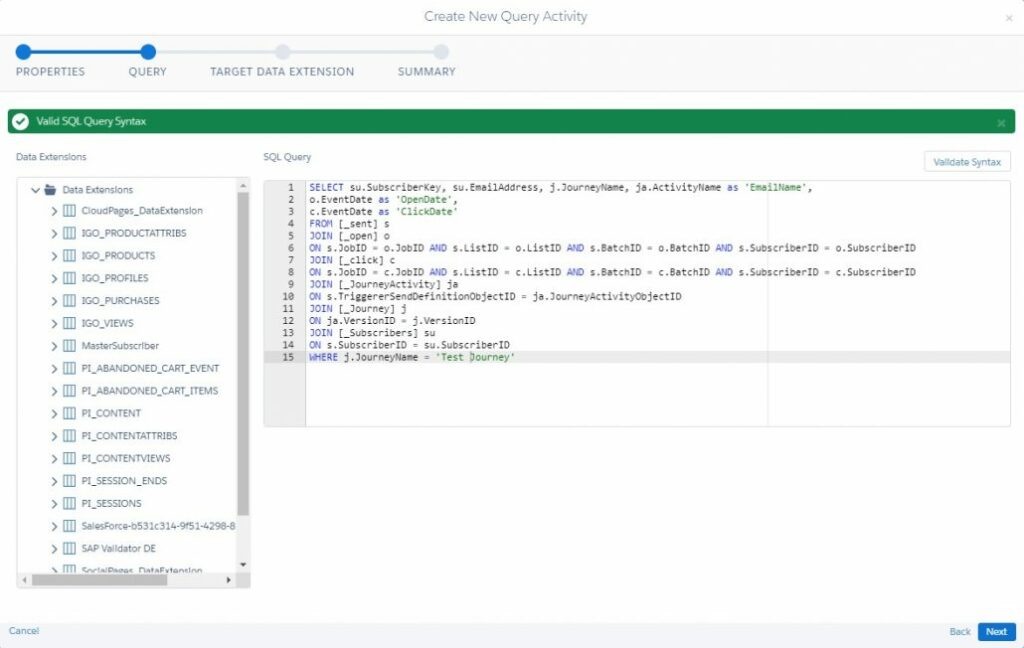
Using tracking data allows for realization of a wide range of practical marketing tasks that make the lives of marketers much easier and definitely more efficient.
As in the example above we can create segments for those who clicks on appropriate link or hovers over right part of the message and target them with a topic-relevant and personalized email the next day and those who skipped clicking can be targeted sometime later in order not to overburden our audience.
So, as you can see Marketing Cloud is a pretty powerful tool for implementing different types of segmentation.
We can create segments based on behavior, activity or views and target our audience with relevant up-to-date messages to unlock customer insights and get meaningful marketing outcomes.
We will dive deeper into Audience segmentation and Einstein Segmentation in another article.
Ready to innovate your business?
We are! Let’s kick-off our journey to success!