How to set up an effective Microsoft document management ecosystem.
Document management, the center of efficient work, is more complex than ever. Businesses grapple with vast amounts of information spread across various storage locations. This challenge is also driven by the rise of remote and hybrid work models. In fact, a recent Gartner study found that the majority of survey participants (66%) believed that providing standardized, IT-supported applications and devices would improve business results.
Microsoft 365 offers a powerful solution to address information silos. Its suite of integrated tools provides document storage and an all-encompassing capabilities for managing the entire document lifecycle, from creation to archival. Driven by the deployment of Artificial Intelligence (AI), this system is critical for modern businesses. In this guide, we’ll explore how to use Microsoft 365 to build an impactful document management strategy.
Document management in Microsoft 365: core components
Microsoft 365 has a tightly integrated set of tools designed to transform the way you handle documents across their entire lifecycle. Let’s break down the key pieces of this system:

SharePoint Online
SharePoint Online is the foundation for building document repositories that are accessible throughout your organization. Think of it as your company’s intranet with robust document management capabilities. Here’s a deep dive into how Microsoft SharePoint empowers enterprises to streamline their document lifecycles:
- Centralized document libraries with rich metadata
SharePoint enables organizations to create structured repositories adjusted to their departments, projects, and business functions. Metadata tagging allows users to categorize documents with custom fields like project codes, document types, authors, or status. This advantage transforms document collections into searchable, filterable assets, and facilitates quick retrieval even within vast company knowledge bases.
- Version control for collaboration and compliance
Every document change in SharePoint is saved as a version and shows previous changes. This feature allows for easy recovery of past versions, prevents accidental overwrites, and serves as an essential audit trail in highly regulated industries.
- Co-authoring and real-time collaboration
Team members can edit the same Microsoft Office documents within SharePoint simultaneously. Changes are reflected in real-time.
- Granular permissions and security
SharePoint offers robust access control at the site, library, folder, and individual document level. Administrators can define roles like ‘view only,’ ‘edit,’ and ‘full control,’ aligning access with specific job functions. This strength enables secure collaboration across teams, departments, and external partners, as well as safeguards sensitive information.
- Automated workflows with Power Automate
Microsoft Power Automate integration with SharePoint unlocks new possibilities for workflow automation. Documents can send approval requests, update metadata based on content, or move files between libraries based on their status. It reduces manual tasks and enforces compliance processes.
- Integration with Microsoft Teams
SharePoint libraries can be integrated directly within Microsoft Teams channels. In this way, they keep relevant documents alongside conversations about a project and create a context-aware workspace for teams. Also, Power Automate approvals can be managed within Microsoft Teams. This makes it possible for users to react to requests and provide sign-offs in the same workspace.
- Advanced search and content discovery
Powered by Microsoft Search, SharePoint goes beyond keyword matching. AI-powered search surfaces results based on document content, metadata, and past user activity, and helps them quickly find relevant information.
- Customization and enterprise integration
SharePoint is also highly extensible. Enterprises can build custom web parts, tailor workflows to specific requirements, and integrate SharePoint with their line-of-business applications. This flexibility guarantees that this document management solution aligns with unique processes of an enterprise.
In order to maximize SharePoint Online’s value, organizations need to invest in user training, change management, and a clear information governance strategy. SharePoint’s power lies in its adaptability, but that requires thoughtful planning of how it will support different teams in the organization.
Explore how we helped our partner migrate from legacy tech to SharePoint Online and on-premise. Success story
OneDrive for Business
OneDrive for Business acts as your individual cloud storage within Microsoft 365. It is perfect for storing personal work files, drafts, and documents in progress. Here’s why:
- Personal workspace with wide accessibility
OneDrive for Business is convenient for drafts, works in progress, or files that are not yet ready for wider collaboration. Crucially, the OneDrive sync client makes these files accessible from any device with an internet connection, which enables uninterrupted work on the go and protects data by keeping it in the cloud rather than solely on local devices.
OneDrive does not exist in isolation. Integrated sharing features allow users to easily share specific files or folders with colleagues. It facilitates quick feedback, targeted collaboration, or handover of finished work to the wider team without necessitating premature placement in a SharePoint site. Fine-grained permissions empower users to control who can simply view versus edit a document.
- Version history and offline sync
OneDrive saves past versions of files and supports recovery from accidental edits or overwrites. Offline synchronization is especially valuable for users who may need access to critical files on flights or in areas with spotty internet.
- Foundation for co-authoring
Integration with Microsoft Office applications makes OneDrive a convenient place to start new documents for collaboration. Real-time co-authoring lets multiple users simultaneously edit Word, Excel, or PowerPoint files stored in OneDrive.
OneDrive will soon offer AI-powered features where users get new information or summary files with Copilot . These features add a layer of intelligence to a user’s personal workspace.
While OneDrive is powerful, enterprises need to balance its flexibility with governance considerations. Clear guidelines on which types of documents should reside solely in OneDrive versus being migrated to SharePoint are crucial. Admin controls can limit external sharing or enforce device policies. Training should emphasize OneDrive’s role as a stepping stone towards broader collaboration within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem.
Teams
Microsoft Teams has risen as a hub for communication and real-time collaboration, but its document management capabilities are often underestimated. Let’s analyze how enterprises can leverage Teams to alter the way they work with documents:
Each Team and its associated channels have a built-in “Files” tab. This feature keeps documents connected to the conversations and tasks relevant to that particular team or project. It reduces the need to search for files in separate repositories and maximizes focus.
- Collaborative work-in-progress
Teams is great for documents that are being actively created or changed. Multiple team members can work on the same file at the same time and see each other’s edits happen live. This is perfect for brainstorming or projects with tight deadlines.
- Smooth integration with SharePoint
While documents live within Teams, they often have a larger lifecycle. Teams transparently integrates with SharePoint. Files are backed up to SharePoint libraries. It fosters a smooth hand-off of files as they mature into more formal, organization-wide assets.
- Reduced information silos
Teams often span departments or functions. Bringing documents directly into the workspace promotes transparency and knowledge sharing across teams. For instance, project updates, status reports, and meeting minutes that reside directly within the project channel can become valuable knowledge resources across the organization.
- Document-centric conversations
Comments and discussions attached to documents within Teams provide context and a threaded history around the changes made. It becomes especially valuable for the onboarding of new team members or analysis of past decisions.
Teams excels when document collaboration is tightly linked to the ongoing work of a group. For long-term knowledge repositories or company-wide documents, SharePoint often remains a better fit, where the focus is on discoverability and the organization in general.
Summing up, the beauty of Microsoft 365’s document management lies in its ability to transform files from static assets into dynamic, collaborative resources. The interconnectedness of SharePoint Online, OneDrive for Business, and Teams provides a fluidity that general-purpose file storage software often lacks. Version history becomes a robust audit trail, not just a safety net. Metadata tagging adds valuable context and makes search results feel curated rather than simply matched.
This integrated approach subtly shifts the focus from mere document organization to a more knowledge-centric workflow. It’s less about merely storing information and more about facilitating its evolution and maximizing its potential impact across the company.
How to build a Microsoft document management system
Streamlining document management in Microsoft 365 does not have to be complicated. While the platform offers robust customization options, you can establish a solid foundation surprisingly easily. In this section, we’ll cover the essential steps to get you started, with a focus on managing the flow of your documents and creating an organized information structure.
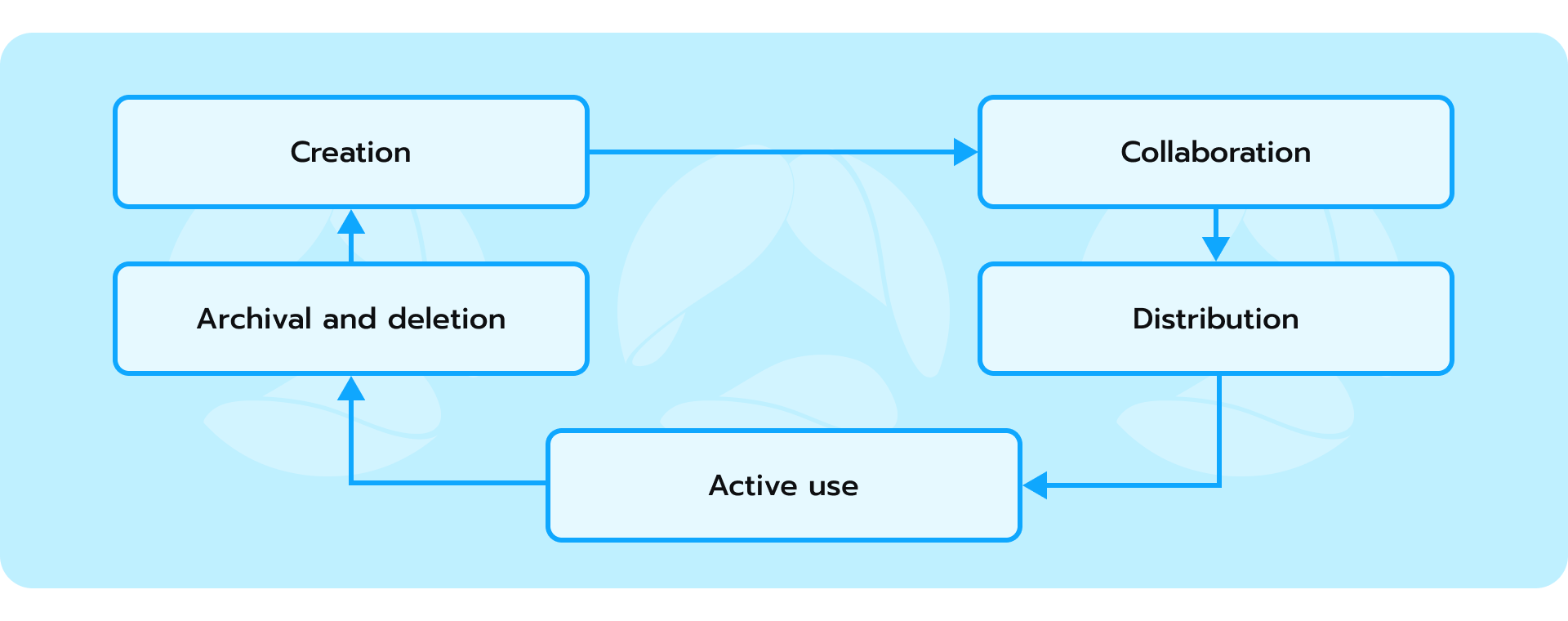
Document lifecycle
Within Microsoft 365’s ecosystem, documents embark on a well-defined lifecycle, from creation to eventual archival or deletion. Initially, a document may start in OneDrive for Business as a personal draft or a collaborative effort within a small group. As it matures and gains relevance to a wider team, it is possible to migrate the document into a designated SharePoint site. This centralized repository allows for structured storage and the application of metadata for searchability and categorization.
Throughout its active life in SharePoint, the document may undergo multiple revisions and collaborations, facilitated by co-authoring and transparent version history. Microsoft 365 even allows for sensitivity labels to be applied, which adds a layer of protection based on the document’s content. When the document’s immediate relevance wanes, it might be designated as a record, which guarantees its preservation or placed under a retention policy, dictating a clearly defined lifespan aligned with either business or regulatory requirements.
Finally, as documents reach the end of their active use, retention policies and data governance come to the forefront. Microsoft 365 provides tools to automate archival, implement deletion schedules based on sensitivity and regulatory requirements, or even apply legal holds if needed. This approach to the document lifecycle ensures both the accessibility of active information and the security and compliance of data at rest.
Information architecture
For large enterprises grappling with vast amounts of information, a well-defined information architecture (IA) is the difference between organized efficiency and chaotic sprawl. It rests on three pillars: users, content, and access.
Users are the heart of the equation. Understanding their needs, search patterns, and workflows is paramount. An IA that prioritizes intuitive navigation and clear labeling empowers users to find what they need quickly, which maximizes productivity and engagement.
Next comes content. Information within the system needs to be categorized logically, using a taxonomy that reflects the organization’s structure and terminology. Think of it as categorizing books by genre and subgenre. This not only makes browsing easier but also facilitates the application of metadata tags and further enriches content discoverability through advanced search functions.
Lastly, access controls become vital within a clear IA. Sensitive information needs protection, while project teams require seamless access to relevant documents. Microsoft 365’s permission settings, coupled with strategic folder structures, allow for granular control. The right people have the right access at the right time, which creates a situation where information security does not hinder collaboration.
Document management strategy
A document management strategy is a complex undertaking, but one that reaps significant dividends for any business. A well-designed strategy brings order into processes and streamlines workflows. Within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, organizations have a potent set of tools at their disposal to beef up their document management. Here are several steps that are essential along this journey:
1. Think about document lifecycle
Consider the different stages a document may pass through (creation, active use, etc.). Determine how this will be tracked and managed within your system.
2. Define document management structure and metadata
The foundation of a sound document management strategy lies in establishing a clear taxonomy and metadata system. This involves outlining how documents will be classified (e.g., by project, department, document type) and what additional information (metadata) will be used to identify and categorize them.
3. Plan your metadata
How do you classify and find your documents? Consider these key pieces of information: project names, client details, and document types, etc. Designate these as metadata fields in SharePoint, paying attention to consistency.
4. Set up permissions
Secure your information from the get-go. Decide who needs what level of access (view, edit, full control) and map those to SharePoint groups and OneDrive sharing settings. This will involve balancing security needs with collaboration requirements.
5. Establish naming conventions
Simple but powerful: consistent file naming (think project code, date, document type) makes search incredibly effective. Roll this out as a company-wide guideline.
6. Leverage Teams
If you’re already using Microsoft Teams, tie in document storage directly to your teams and channels. This keeps communication and relevant files in one place for efficiency.
7. Train your users
The best system fails without adoption. Provide clear guidelines on document storage locations, naming, and sharing best practices. Consider short training sessions or easily accessible documentation.
It is important to remember that document organization is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. As your business needs change or new Microsoft 365 features emerge, revisit your structure and processes. Some of these updates might introduce new organizational tools or refine existing ones. Staying informed allows you to use these advancements and optimize how you manage documents within the platform.
Practices for effective document organization
Transforming your Microsoft 365 environment to a well-organized information hub leans on a few strategic practices. A thoughtful approach to document organization directly impacts how users find information, collaborate on projects, and extract value from your company’s knowledge base. Let’s delve into insightful strategies and best practices that will help you optimize your document management within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem:
- Develop a clear folder structure
Map out a logical hierarchy for SharePoint sites and OneDrive based on departments, projects, or other relevant categories. This approach creates an intuitive navigation system for users.
Tag your documents with relevant keywords, categories, or other custom fields so as to make them easily discoverable through search and filtering within SharePoint.
- Deploy naming conventions
Establish a standard for naming files that includes key information like project codes, document types, and dates. It will make search and filtering far more effective.
- Establish a retention policy
Not all documents need to be kept forever. Implement retention schedules to automate archival or deletion of documents based on their age or sensitivity. This avoids clutter and reduces legal risks.
Microsoft 365’s evolution is accelerating with novel AI-powered tools like Copilot. These advancements signal a shift where your document management system goes beyond being a mere repository and becomes a dynamic, intelligent asset. Copilot’s ability to generate summaries, suggest relevant content, and assist in drafting will smoothly integrate into your document workflows.
Security and compliance in Microsoft 365
Microsoft 365 offers granular control over who can access and modify documents within SharePoint, OneDrive, and Teams. Administrators can assign permissions at the site, library, folder, or even individual file level. This capability guarantees that the right people have access to the information they need, while unauthorized access is prevented.
Sensitivity labels act like tags that can be applied to documents, embedding classification and protection settings. For example, a label marked “Confidential” might automatically add encryption and restrict external sharing. It helps users understand the sensitivity of the content they are working with and empowers organizations to consistently enforce protection measures.
Enterprises can set up retention policies to determine how long documents are kept before they are automatically archived or deleted. These rules can be based on factors like document age, sensitivity label, or project completion status. Retention policies streamline information governance and mitigate legal risks stemming from keeping data longer than necessary.
Microsoft 365 includes a dedicated Compliance Center, which provides tools to manage adherence to various data protection regulations. Features like eDiscovery aid in responding to legal requests, while Data Loss Prevention (DLP) helps detect and prevent the inadvertent leak of sensitive information. It’s important to note that configuring Microsoft 365 for compliance requires careful alignment between technical implementation and your organization’s specific regulatory obligations.
Takeaways
For modern enterprises, documents form the lifeblood of operations. Contracts, proposals, invoices, reports – an endless stream of critical information that must be meticulously organized and readily accessible. A document management strategy is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. Since the need for centralized, easily-accessible document management is increasing, cloud-based tools like Microsoft 365 answer this call.
Embrace complexity and find clarity through Microsoft 365 document management: contact us.












