Pros
Microservices architecture, characterized by its modular and independent components, offers benefits such as agility, scalability, easy management, resiliency, and easy onboarding, making it a preferred choice for complex and evolving applications.
- Agility. By splitting the functionality into separate modules and isolating it from other related services, developers can leverage this benefit to accelerate and streamline development processes and be focused only on updating a particular piece of the application.
- Better scalability. If any update is needed, it is optional to redeploy the whole system since each microservice is self-contained, and each element can be scaled independently. Therefore, new components can be added without downtime. Furthermore, this solution provides time and cost-efficiency.
- Easy to manage. As independent deployment artifacts are broken down into modules, a microservice application is easier to understand and, consequently, to manage. Supports horizontal scaling. That means when you need to make alterations to a particular service (for instance, when your app has many users), you can scale out only that microservice responsible for one specific function.
- Resiliency. When there is an issue or bug in a particular microservice, it doesn’t influence other microservices, and they remain unaffected; hence, the app continues its functionality even if something goes wrong, limiting the possibility of generating mistakes due to the isolated nature of modular components.
- Easy onboarding. It is much easier to understand the architecture with distributed services, and instead of working on the whole system, a new developer has to master only a particular microservice.
- Increased revenue. With the possibility of fast iterations and eliminating downtime of the app, users remain satisfied, impacting their retention and loyalty. Therefore, microservices ensure an increase in revenue thanks to efficient approaches toward process management.
- Integration with new technology. Being completely independent of each other, microservices offer flexibility in selecting new technology or framework. Therefore, microservices are designed for business and technological capabilities. In contrast to the monolithic approach, microservices are open in adopting new technology stacks to solve certain business purposes.
While microservices provide flexibility and scalability over container systems, they also introduce complexity, security concerns, higher operational costs, and challenges in handling cross-cutting concerns, debugging, and testing.
Cons
In contrast to the entire monolithic application architecture, microservices do not limit the business capabilities of the development team in size and scope, providing the capability to be integrated with other services and different tech stacks. Nevertheless, there are still drawbacks to the microservices approach, mainly related to its complex nature. Let’s go through some of them:
- Complexity. Since the number of independent components in microservices apps is increased compared to monolithic applications, managing many distributed services at scale with their separate databases is a complicated task. The microservices approach requires a team of developers responsible for each service.
- Less security. Inter-services communication within the network makes microservices applications less secure.
- Higher operational costs. They are typical. Deploying microservices generates additional units, increasing management and operational cost overheads.
- Cross-cutting concerns. In a microservices architecture, handling cross-cutting concerns such as logging, metrics, service registration, externalized configuration, etc., must be done in every service.
- Difficulty in debugging problems. To identify the root cause of the error, developers have to inspect each service log independently, which leads to a workload increase.
- Complicated testing. It is challenging to test microservices due to many independent components in contrast to the monolithic approach allowing one to deploy the system locally and try it.
Despite the flexibility and scalability offered by microservices, they come with their own challenges, including increased complexity, security concerns, higher operational costs, and difficulties in debugging and testing, which need to be carefully considered before adopting a microservices-based application.
Recap: which architecture is worth selecting for your business?
To summarize the approaches mentioned earlier, the main advantage of the monolithic approach is easy understanding and quick development of legacy systems. In contrast, the microservices approach allows for scalability and integration of the entire system with any technology. To determine which architecture best suits your project, it is good to formulate situations when you need either a monolith architecture or microservices.
Monolithic applications
With their simplicity and ease of implementation, monolithic applications can be ideal for specific scenarios.
- Since microservices require a solid understanding of complex models, the monolith will be a good option for startup businesses that launch small projects.
- If there are tight timelines and you must roll out your project as soon as possible, a monolithic approach will satisfy your needs.
- After your project’s estimation, your app will need new functionalities in the future and will need to be integrated with the latest technology. If there is no need to upgrade the application, then monolith will be a great solution.
Therefore, monolithic architecture can be suitable for startups, projects with tight timelines, or applications that do not require complex systems or frequent upgrades, or new functionalities.
When do you need microservices architecture?
On the other hand, the microservices architecture, with its scalability and flexibility, is better suited for specific situations.
- The microservices approach requires expertized developers who work according to Agile methodology and can make processes go smoothly without downtime.
- If your goal is to upgrade the application and add new features in the future, microservices can help scale out. Moreover, with technological progress, you, as a business owner, may opt for advanced solutions for your customers and be on top of your competitors. The microservices approach allows you to use different technologies based on your business requirements.
Thus, microservices architecture is an excellent choice for businesses aiming for scalability, future upgrades, continuous deployment, and adopting new technologies, provided they have the expertise and resources to manage the complexity.
Monolithic architecture vs. microservices architecture: comparison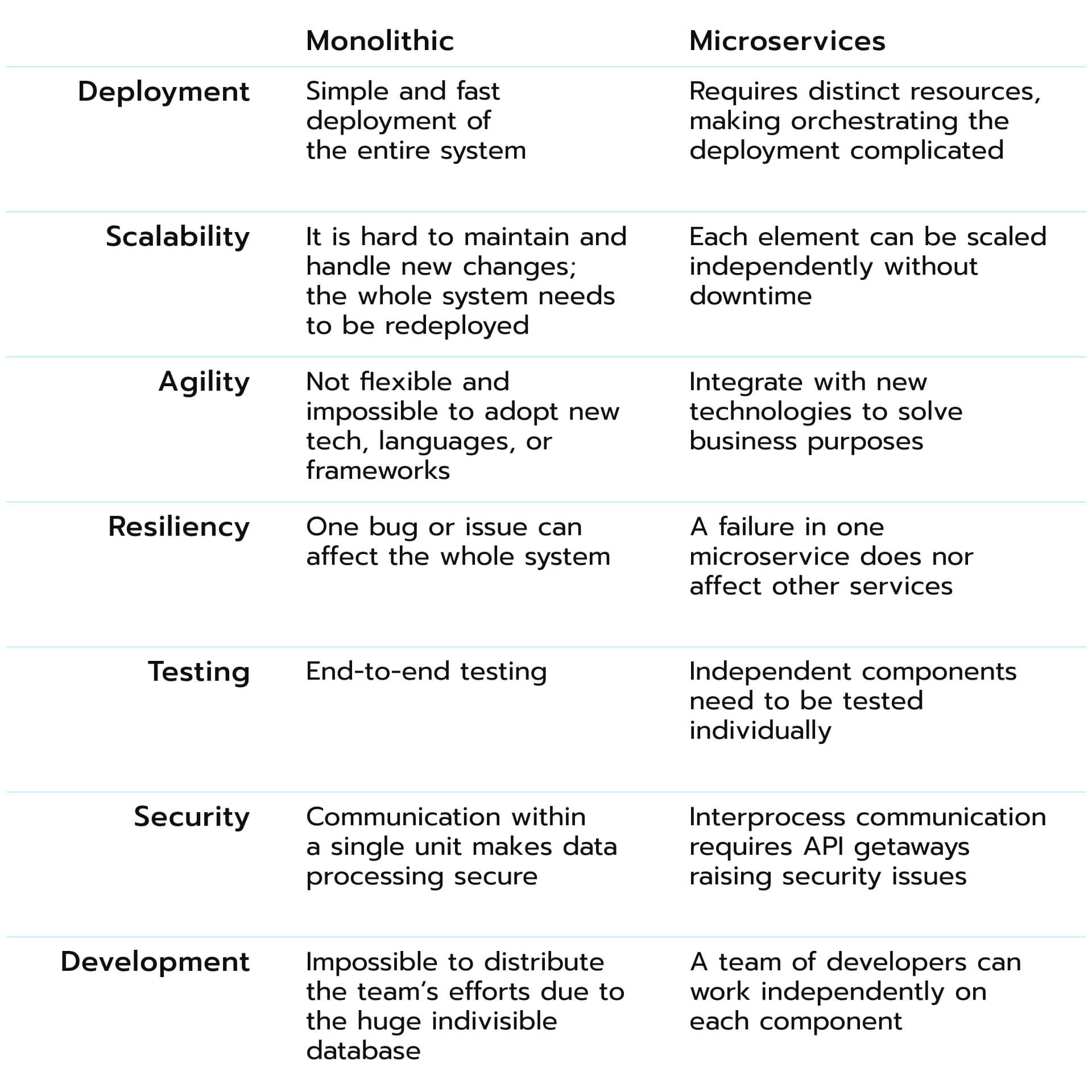 Final remarks
Final remarks
The selection of monolithic and microservices architecture applications the architectural type depends on the organizational structure of your project. A monolithic approach will be more suitable if your business is a startup with a small team of developers. But microservices would be a perfect fit if your goal is to scale your business and you are looking for solutions to upgrade your product.
Microservices are preferable to monoliths due to their capability to manage growing data sets. However, they may not always be efficient for small organizations that do not follow Agile approaches. Therefore, it is essential to understand your business objective and company culture.
What type of software architecture will suit your project? Contact us, and we will provide experts skilled in both approaches, matched with your product and your industry.


 Final remarks
Final remarks






