Driving meaningful connections and enhancing customer engagement in life sciences
Learn about the most critical aspects of customer engagement and how to build and implement a reliable strategy for long-term success.
Starting a telemedicine business can be tough, but a seasoned software development partner can help launch it much quicker.
The COVID-19 outbreak, a worldwide pandemic declared by the WHO, profoundly transformed the healthcare sector. All around the world, people were advised not to leave their homes, and as a result, virtual care and telehealth services experienced unprecedented growth; a 64% surge in 2020.
Telehealth services are the application of technology in furnishing audiovisual communication between healthcare providers and patients. It enables distant care delivery, remote healthcare analysis, patient monitoring, etc. The telemedicine market is expected to grow from $194.1 billion in 2023 to $459.8 billion in 2030 (Figure 1.)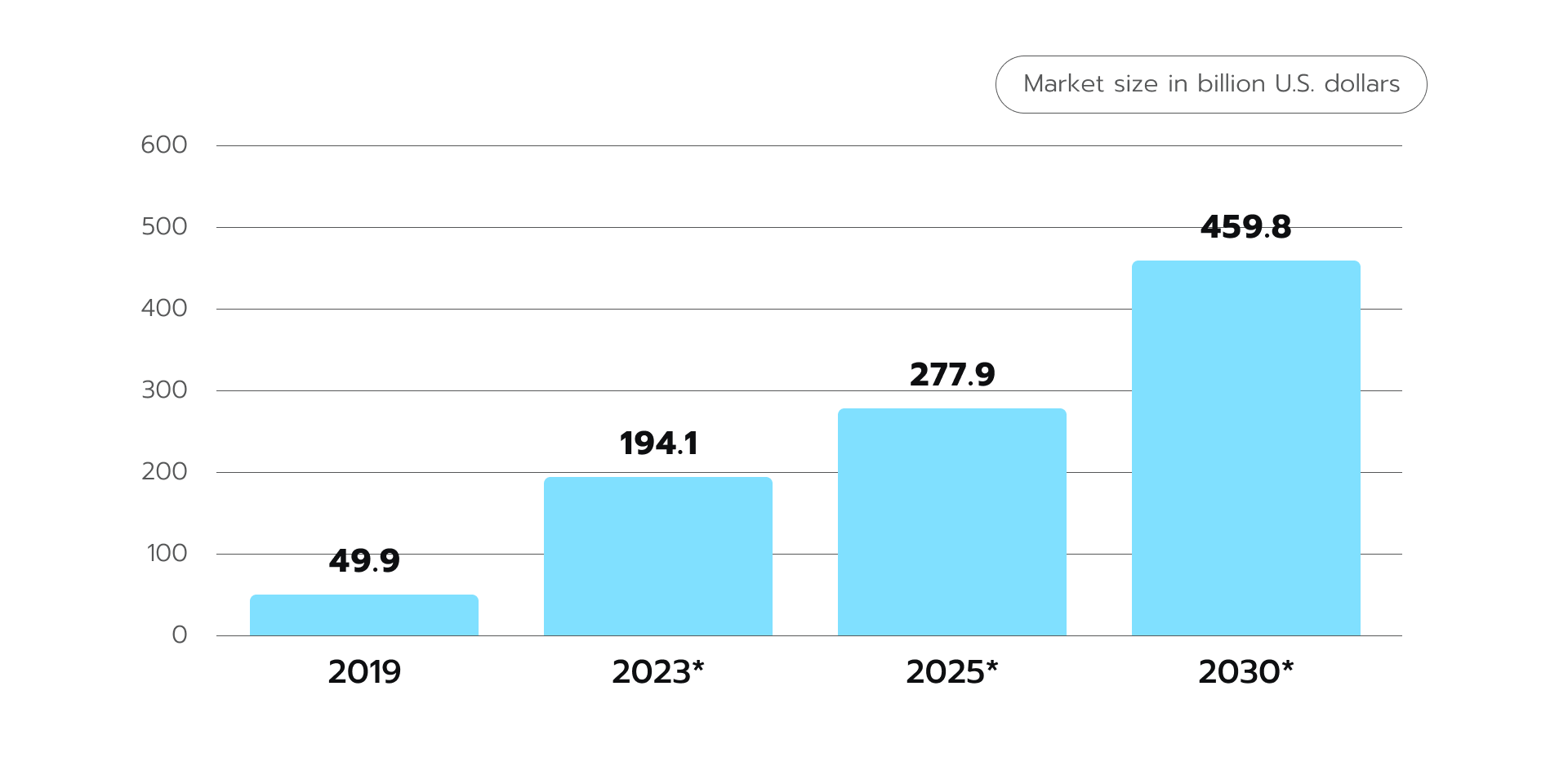 Figure 1. Telemedicine market size
Figure 1. Telemedicine market size
Currently, telehealth apps are used extensively in behavioral health, radiology, cardiology, and online consultations. They dramatically reduce the burden of tasks for healthcare professionals and help organizations cut care costs. In 2021, online video and audio consultations basically became the new norm, and most organizations and medical practitioners don’t appear to be abandoning them, even after the subsiding of the pandemic, due to their associated cost-effectiveness, the absence of outpatient department (OPD) waiting lines, and easy user access. Recently, many healthcare startups have emerged offering solutions and technologies for remote patient monitoring and care delivery.
Moreover, healthcare providers have also been striving to extend their virtual capabilities and start a telehealth business, especially for unique specialties such as mental health, general health, and cardiology. They’ve also been actively undertaking strategic initiatives, such as collaborations and partnerships with software organizations, in order to strengthen and expand their market presence and diversify services.
Spending on healthcare services is rising across the globe due to the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and declining birth rates, as well as the rapidly growing geriatric populations. In the U.S., where healthcare spending reached $4.3 trillion in 2021, it is expected to grow by 45.9% in 2030 (5.1% yearly). And the expectations are similar for the majority of developed and even developing countries. Therefore, there’s an acute need on the side of healthcare providers for technology-driven solutions that can enable the delivery of quality healthcare and at a reduced cost. Since advanced telehealth platforms can fulfill both of these requirements, they’re being actively deployed by healthcare and pharma facilities, even now when COVID-19 is no longer considered an international public health emergency.
When implemented properly, telehealth breaks down the barriers to healthcare delivery in remote and/or previously underserved areas. This is crucial because many people in developed and especially developing countries live in places where there is no easy access to quality medical services. Therefore, governments are increasingly supporting the adoption of virtual care, because it doesn’t incur much cost yet it can offer a wide array of services to these populations. In the U.S., the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has already established several programs aimed at helping healthcare providers implement and deploy telemedicine technologies. In addition to that, various policies and pilot projects are emerging that further fuel market growth there.
Millennials and Gen Z are perhaps the most researched and profiled generations ever to live. Any survey regarding software always confirms their love for technology, translating into a readiness to switch to digitized versions of services quickly, including telehealth.
According to a Massachusetts medical center study, more than half of the people in the 18-29 age group prefer telemedicine to in-person visits (Fig. 2.) Since millennials now represent the largest generational slice of the workforce, healthcare organizations want to capitalize on their enthusiasm for telemedicine as well as inspire older employees to follow suit. Gen Z, arguably even more comfortable with technological solutions, is expected to drive the telehealth market even further once they assert themselves in the workplace. 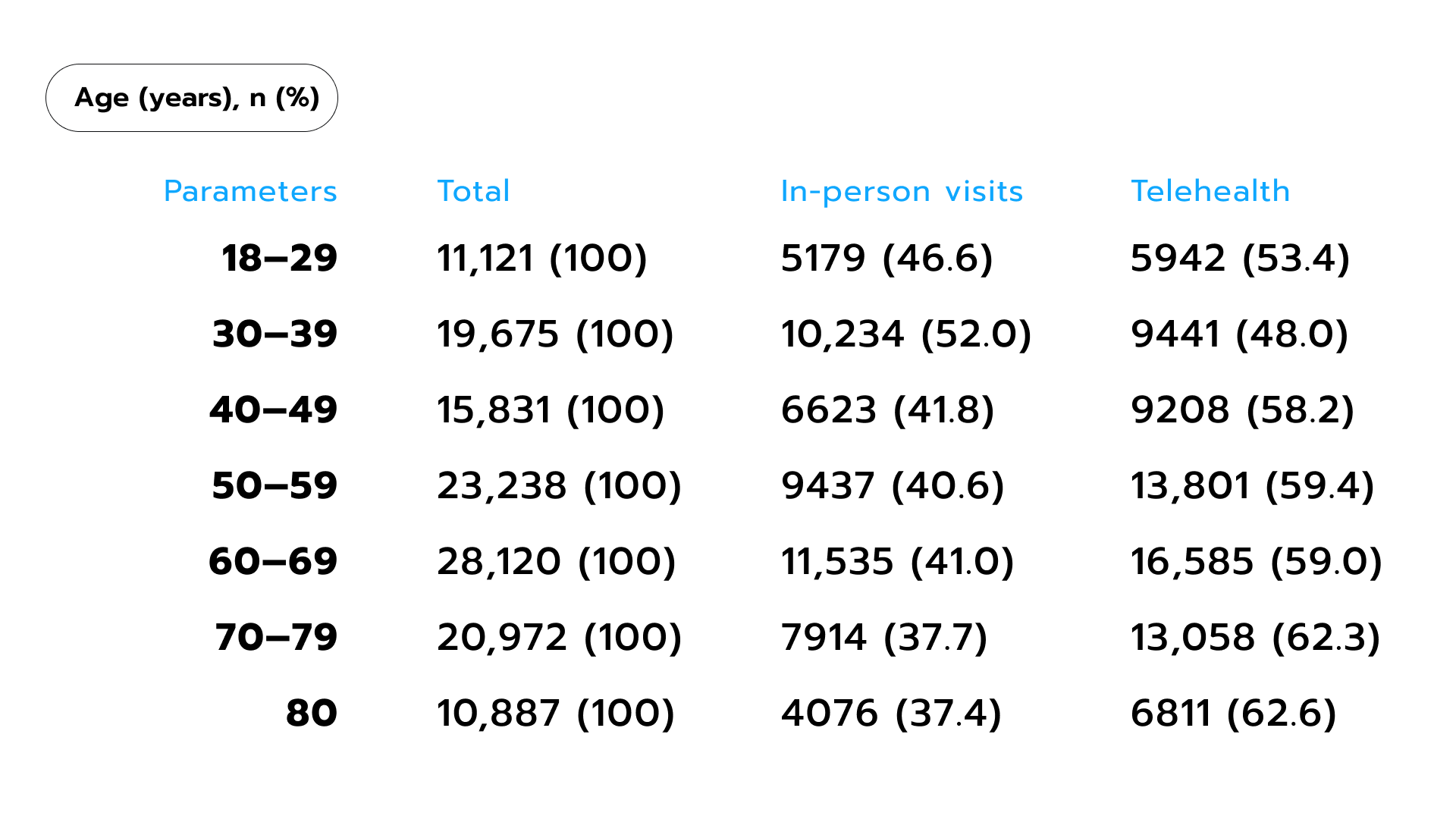 Figure 2. Usage of in-person and telehealth services
Figure 2. Usage of in-person and telehealth services
One of the key restraining factors in telemedicine adoption is the lack of software development, implementation, and integration skills and expertise among healthcare organizations. The reasons for this include:
Reliable connectivity is paramount when it comes to delivering timely and effective telehealth services. The minimum bandwidth required to ensure uninterrupted and efficient provision of services, as per The American Telehealth Association Practice Guidelines, is 384 Kbps. This can, therefore, present a significant challenge in low-and-middle-income countries and even in the poorer rural areas of developed countries where internet penetration might be lacking. However, since we’re now actively seeing both healthcare facilities and governments investing in virtual care programs and initiatives, this challenge is being addressed on several levels.
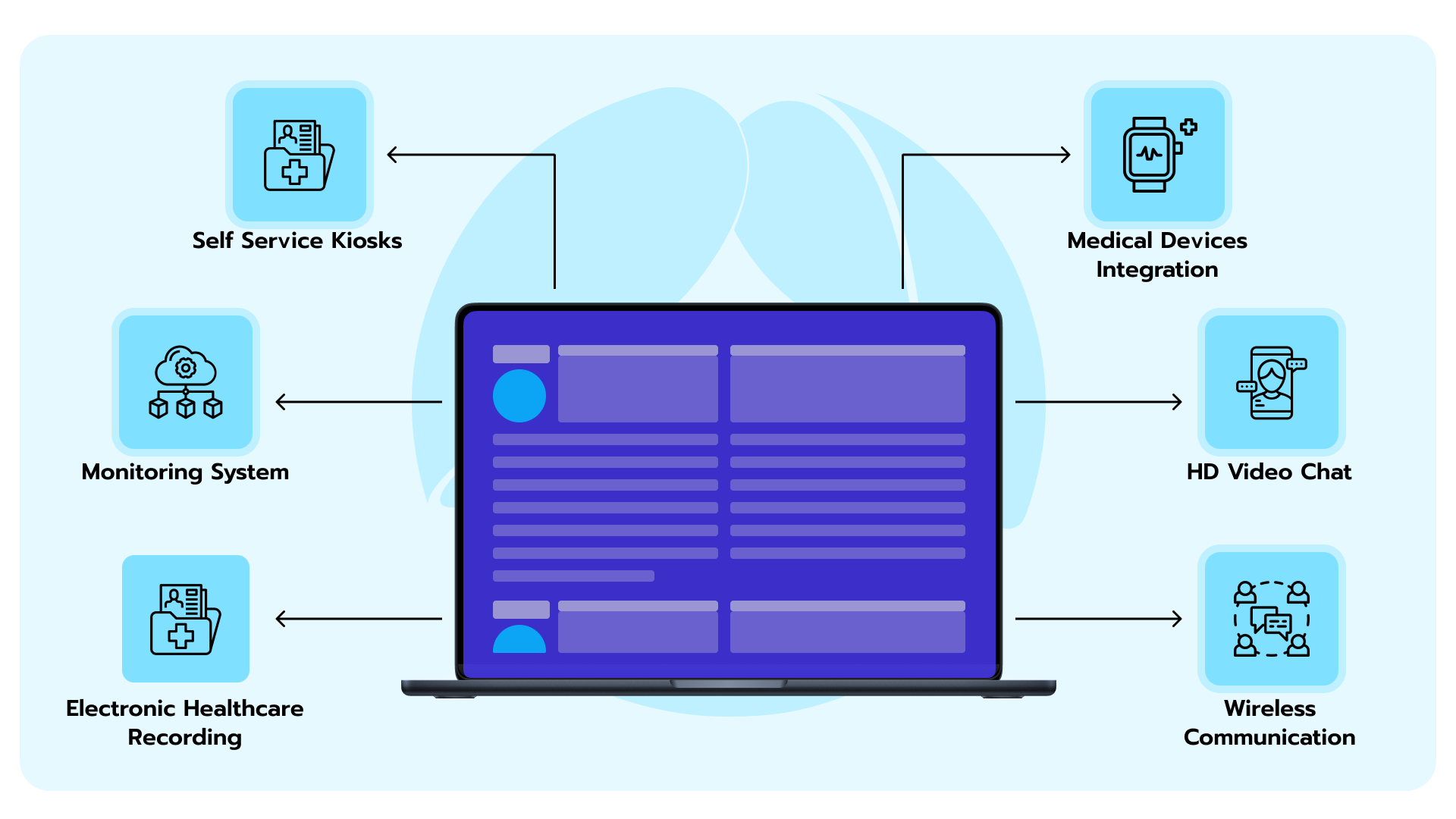
Figure 3. Example of a telemedicine solutions
This is the primary reason healthcare organizations often seek our assistance for their telemedicine projects – they require a service provider with substantial experience in telemedicine-specific platform engineering and a proven track record of relevant projects. So, if you’re also considering launching such an initiative, we recommend that you first ensure that the software company you may be partnering with possesses an intricate knowledge of healthcare workflows, and the specific challenges and barriers associated with virtual patient care. An added bonus would be their experience in designing sleek interfaces for healthcare apps, developing and optimizing video-conferencing platforms, and implementing features such as appointment scheduling, virtual monitoring, prescription management, etc.
The service provider must also be well-versed in cloud computing since most telemedicine apps have a cloud platform at their core, plus modules for streaming, messaging, conferencing, data processing, etc. At Avenga, our experts possess extensive experience in designing cost-effective cloud solutions with carefully selected relevant services, leading to reduced ownership costs. Moreover, a telemedicine application will most likely need to be integrated with a variety of medical devices and sensors, which means the provider’s experience in IoT will certainly be required.
Learn more about how we enhanced the customer experience to improve conversion rates for Klara. Success story
The next step in choosing a vendor would be assessing their experience working with the stringent regulatory requirements and frameworks governing healthcare information. Each telehealth interaction must be safeguarded against breaches, so the team working on your project must have proven experience in data protection and encryption mechanisms. At Avenga, we assist organizations with:
Finally, by selecting the right vendor, you will discover that your collaboration with them evolves from being merely transactional to becoming a strategic partnership, where knowledge sharing plays a pivotal role. Throughout the project’s duration, our clients within the healthcare field have the opportunity to acquire expertise in development, system architecture, software upgrades, and maintenance from us. Moreover, we offer extensive workshops and training sessions to many of them.
The skillsets that companies can acquire through this interaction are invaluable for future technology projects. Furthermore, equipped with advanced software practices, our clients’ staff can make substantial contributions to ongoing improvements and process optimization. Additionally, they will possess enhanced capabilities for troubleshooting technical issues and fostering rapid innovation within the realm of digital healthcare.
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, the telehealth market has been on the rise. Small and large healthcare organizations are now actively entering the arena, supported by various new government programs and policies, and are encouraged by the increasing demand for telemedicine services.
However, for many companies, starting a telemedicine business or transitioning into the digital sphere might prove too challenging to undertake on their own, so they hire technology companies to partner with them. When finding a reliable software development vendor, healthcare providers should focus on the candidate company’s experience in telemedicine platform engineering, healthcare security, and governing compliance requirements (i.e., HIPAA, HITECH, CCPA, and GDPR), as well as being proficient in cloud computing.
If you’d like to learn more about how to launch a successful telemedicine app and improve health outcomes, don’t hesitate to contact our experts.
Ready to innovate your business?
We are! Let’s kick-off our journey to success!