How to drive automation with this reliable data storage.
Dataverse is right at the heart of Microsoft Power Platform. As an embedded data storage capability, it tackles common challenges with traditional data management: scattered information and insufficient access to data. Dataverse solution enables organizations to use their data effectively within the Power Platform, empowers them to build custom applications, and automate processes with greater speed and efficiency. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the core concepts of Dataverse and explore different scenarios where it can be the key to solutions tailored to your industry.
What is Dataverse in Power Platform?
Formerly known as Common Data Service (CDS), Dataverse is the unassuming yet powerful data storage in the Microsoft Power Platform. It is a secure data service that helps enterprises store and manage data from various Power Platform applications like Power Apps, Power Automate, or Power BI in the cloud. Dataverse also offers relationships between tables (e.g., a customer record linked to their orders), much like you’d find in traditional relational databases.
Figuratively speaking, it resembles a central nervous system of Power Platform solutions. IT professionals will find here familiar concepts – data is structured in Dataverse tables (entities) with columns (fields) that define data types. Also, Dataverse goes beyond basic storage. It has reliable security features and allows for granular control over access and permissions, which integrates effortlessly with Azure Active Directory. This strategy means that your sensitive business data remains tightly guarded.
Dataverse’s primary strength lies in its integration with the rest of the Power Platform as it connects various components. Data from multiple sources, such as internal databases, SharePoint lists, or external APIs, can be smoothly ingested into Dataverse through Power Query. With Dataverse, it is possible to set up a unified data model that can be leveraged by any Power Platform application. Imagine building a customer service app that pulls data not just from your CRM system but also from SharePoint customer feedback surveys. Dataverse makes this data mashup easily accessible.
Another integration greatly contributes to the solution’s capabilities. Dataverse can be the underlying data platform for Dynamics 365. Dynamics 365 users can interact with Dataverse data through the user interface of their specific Dynamics 365 application (Sales, Customer Service, Marketing, etc.). They create, read, update, and delete records, with no need to know the technical details of Dataverse. At the same time, these users can utilize tools like the Power Apps maker portal or the Dynamics 365 Customization interface to create custom tables, fields, forms, views, and business processes in Dataverse.
For IT experts, the solution offers a familiar and powerful data platform. Customizable security models, support for plugins and workflows, and even a RESTful API unlock new vistas of possibilities. For example, if you need to enforce specific business rules on your data, Dataverse alleviates this process. Similarly, if you want to integrate your Power Apps with a custom web service, you can find a solution with Dataverse.
Learn how we modernized a SharePoint intranet environment that operates across 180 countries. Success story
The value of Dataverse integration
For employees, Dataverse brings a distinct advantage: it streamlines access to the information they need. Instead of hunting for information across spreadsheets, legacy systems, or email threads, they can access data from various systems in a single platform. Combined with Power Platform tools, this centralized repository powers user-friendly apps that are adjusted to specific job roles. This benefit translates into decreased time allocated to a search for data. According to the Gartner survey, 47% of digital workers find it challenging to find relevant information or data necessary for their job (see Fig. 1). Dataverse can partly alleviate that hurdle.
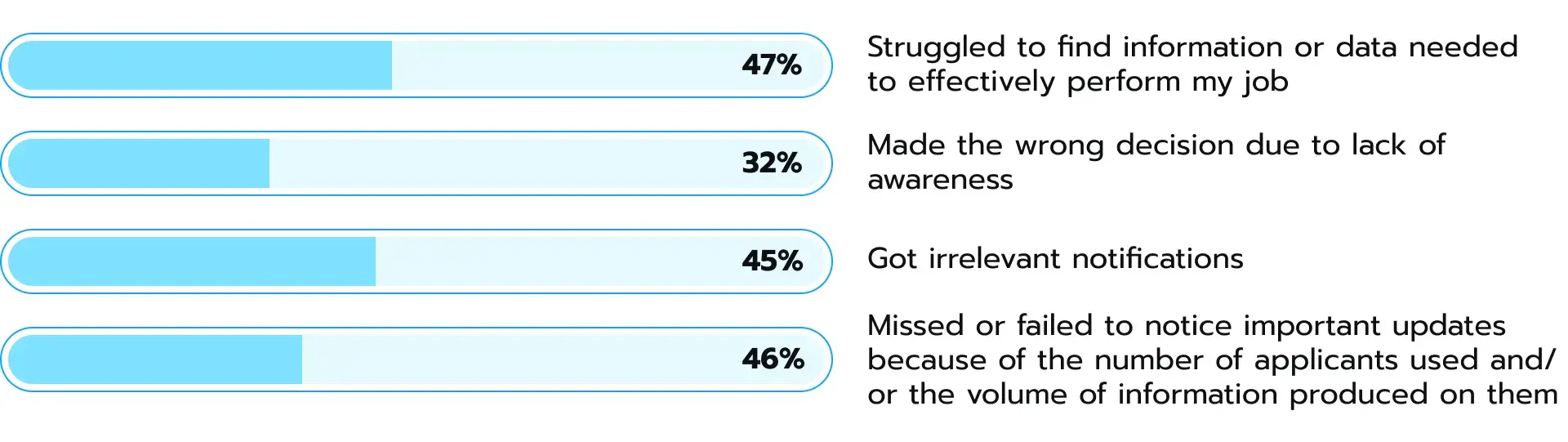 Figure 1. The search for the right data becomes increasingly challenging for employees, creating a strong need for improved digital employee experience (DEX) tools, as Gartner suggests.
Figure 1. The search for the right data becomes increasingly challenging for employees, creating a strong need for improved digital employee experience (DEX) tools, as Gartner suggests.
Below are key strengths essential to Dataverse’s functionality:
1. Simplified data management
As a centralized repository, Dataverse eliminates the need to juggle multiple databases or spreadsheets. For common business scenarios, it provides pre-built data models and saves employees the effort usually spent on designing tables and relationships from scratch. However, its greatest asset is its integration with the Power Platform ecosystem. Data in Dataverse becomes immediately accessible to your Power Apps, Power BI dashboards, and Power Automate flows. This capability translates into smoother data flow and a consistent user experience across your applications. This unified data can also become the lifeblood of automation.
Key advantages:
2. Improved security and compliance
With adherence to various data regulations and cybersecurity concerns embedded in its functionality, Dataverse relies on a strong foundation for securing your business data. It offers flexible, role-based access controls that make sure users see the data they’re authorized to. For sensitive information, granular field-level security can be applied. Auditing and change tracking help maintain accountability and meet compliance standards. Dataverse’s compliance with industry standards such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is another crucial aspect of data protection for enterprises.
Key advantages:
As we mentioned earlier, Dataverse drives automation in enterprises through its alignment with other Power Platform tools. Here are several use cases that may come in handy to your business:
- Customer onboarding. A new contact created in Dataverse can trigger a Power Automate flow to send welcome emails, create tasks in a project management tool, or generate relevant documents for a customer.
- Inventory management. Product stock levels falling below a threshold in Dataverse can initiate an automated purchase order creation, send alerts to warehouse managers, and update relevant dashboards.
- Lead qualification. New leads in Dataverse can be scored based on their information, and Power Automate can automatically assign them to sales reps, schedule follow-up calls, or nurture them with targeted email campaigns.
Finally, Dataverse empowers rapid development owing to the Power Platform’s low-code/no-code philosophy. With this Microsoft 365 solution, “citizen developers” can build custom apps and automate processes without extensive coding expertise. The rich metadata provided by Dataverse makes data discovery and understanding far more intuitive. This metadata describes fields, relationships, and business logic, and enables quicker app design. The potential for reusing components further streamlines development; there is an option when a workflow created in one app can be easily repurposed in another, which substantially cuts down development time.
When to use Dataverse
The appropriate data foundation plays a crucial role in the ultimate success of Power Platform solutions. While Dataverse offers undeniable advantages, it’s equally important to understand when it’s the most suitable choice. Here is a brief guideline on scenarios that are best suited for Dataverse integration:
- Power Platform-centric solutions
If you’re heavily invested in building apps with Power Apps, Power Automate, or Power BI, Dataverse becomes a natural fit. It’s engineered for seamless integration, simplifying your data layer.
- Insights and historical data
For storing, analyzing, and drawing insights from data over time, Dataverse’s structure is an excellent choice.
- Offline capabilities
If Power Apps need data access even when offline, Dataverse allows you to configure apps for offline availability.
- Security and compliance
When robust role-based security, auditing, and industry certifications are critical for your application, Dataverse provides a reassuring level of control and compliance.
When to consider alternatives
- Direct integration with existing systems. When you need to pull or push data directly from well-established SaaS platforms (Salesforce, SharePoint, Dropbox, etc.), pre-built connectors offer a seamless way to integrate them into your Power Apps and Power Automate flows.
- Real-time data needs. If your solution depends on immediate updates from an external source (e.g., real-time stock prices), connectors provide the most direct path for accessing the latest data.
- Existing enterprise data warehouse: If you already have a mature enterprise-level data warehouse, integrating it with Power Platform tools might be a better choice than replicating that data entirely within Dataverse.
It’s important to note that it’s not always a matter of one option versus another. Different solutions can lean on a combination of connectors to bring in external data and Dataverse to store core business entities and apply customized processes. For example, your company can pull in customer data from Salesforce through a connector and then store it in Dataverse along with additional relationship data specific to your business.
Dataverse solutions explained
When it comes to citizen development within the Microsoft Power Platform, Dataverse solutions are mechanisms for packaging and deploying customizations and configurations between different environments. Dataverse solutions provide a user-friendly way for citizen developers to manage and promote their customizations across environments without relying heavily on IT professionals. This is crucial in scenarios where changes made in a development or testing environment need to be transferred to a production environment.
Why Dataverse solutions are important:
- Transporting changes. Solutions are the primary means to move customizations between different Dataverse environments (e.g., development, testing, production).
- Modular development. They allow for organizing work into logical units, which improves collaboration and maintainability.
- Dependency management. Solutions track dependencies between components and support consistent deployment.
- Version control. They help keep track of changes over time.
Here’s the general process of how to get changes from one environment to another:
| Create a solution |
In the source environment, create a new solution and add the desired components to it. |
| Export the solution |
Export the solution as a managed or unmanaged package. |
| Import the solution |
In the target environment, import the exported solution package. |
Governance
In the context of Dataverse, governance is an umbrella term that covers policies, processes, and tools implemented to guarantee the data’s efficient and compliant use. Here are the critical aspects of Dataverse governance:
Data security and access control
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
Define granular permissions within Dataverse and specify who can access certain data entities (tables) and what actions they can perform (read, write, delete).
- Data loss prevention (DLP)
Use DLP policies to prevent sensitive data from being accidentally or maliciously exported from Dataverse.
- Auditing and logging
Enable auditing capabilities within Dataverse to track user activity and data modifications. This creates a record of who accessed what data and when, crucial for security analysis and compliance purposes.
Data quality and management
- Data validation rules
Set up validation rules within Dataverse to support data accuracy and consistency. These rules can enforce data types, define acceptable value ranges, and prevent invalid entries from being added.
- Standardization and naming conventions
Establish clear naming conventions for entities, fields, and relationships within Dataverse. This promotes data discoverability and facilitates easier understanding of your data model.
- Data lifecycle management
Create policies for data retention, archiving, and deletion within Dataverse. This quality guarantees you comply with regulations and maintain a clean and efficient data environment.
Implementing strong Dataverse governance might seem daunting, but the investment is well worth your time. A well-governed Dataverse environment translates into increased efficiency and greater user confidence. Clear ownership of data reduces confusion and bottlenecks within your organization, while robust security measures minimize the chance of data breaches or compliance violations. Most importantly, good governance fosters trust in your Power Platform solutions and encourages widespread adoption.
Security model
Dataverse is responsible for a flexible security posture designed to fit within a modern enterprise environment. It relies on Azure AD for identity and access management. This means your existing Azure AD users and groups become the gatekeepers of your Dataverse data. You can control access to Dataverse environments, applications, and data through familiar Azure AD tools.
Dataverse employs a role-based security system. Pre-defined roles (e.g., System Administrator, Salesperson) come with a set of permissions, and you can also create custom roles tailored to your organization’s structure. These roles govern what actions a user can create, read, update, delete records, and so on. Users can be assigned multiple roles, with their effective permissions being the combination of those roles.
Sometimes, an organization’s security needs expand beyond simply controlling access to an entire table (entity). Field-level security allows you to limit the number of users who can read, update, or create permissions on specific fields within a table. This is essential for scenarios that involve sensitive data like personally identifiable information (PII) or financial records.
The security model of Dataverse provides IT teams with a familiar, fine-grained way to manage user access and safeguard data. This secure foundation and its alignment with Azure AD make it the right choice for organizations that place high importance on protecting their business information.
Migration to Dataverse
Migrating to Microsoft Dataverse brings companies potential advantages in data consolidation, security, and development efficiency. A successful transition hinges on a well-defined migration plan. Let’s explore common migration scenarios, available tools, and best practices to streamline the process.
After an assessment of their data sources, enterprises determine the most suitable migration path. Options include:
- Legacy systems
Data migration through ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes using tools like Azure Data Factory or Power Query.
- Microsoft Access/Excel
Direct migration using built-in tools within Power Platform, with focus on data quality checks and potential schema refactoring.
- Existing Dataverse environments
Dataflows within Power Platform enable controlled transfer of configurations and data between Dataverse environments (e.g., dev vs. production).
There are several key nuances enterprises typically consider before migrating to Dataverse:
- Existing integrations
Factor in how existing systems and applications interact with your current data store. You’ll need a plan for re-pointing these integrations to Dataverse or potentially replicating certain data to bring seamless operation after migration.
- Skills and resources
Evaluate your in-house expertise with Microsoft Dataverse and the Power Platform. Determine if additional staffing, training, or external consultancies might be required to support a successful migration project.
- Cost-benefit analysis
Conduct a thorough analysis to compare the costs associated with migration (potential licensing, development, maintenance) to the anticipated long-term benefits Dataverse aims to bring your organization.
When it comes to migration to Dataverse, a critical best practice is to start small. Begin with pilot projects that focus on a specific subset of your data. This controlled approach reduces risk and allows you to identify potential challenges, fine-tune your processes, and gain valuable insights before undertaking a full-scale migration.
In addition, it is crucial to prioritize user training. As your applications and data access methods shift to a Dataverse-based solution, prepare your users for these changes in advance. Proactive training will ease the transition, minimize disruptions, and contribute to the overall adoption and success of your new Dataverse-powered applications.
Takeaways
Dataverse empowers companies to build end-to-end business processes. Its intuitive structure and reliable security features, as well as integration capabilities, make it a valuable asset for any organization striving to leverage low-code development tools in Power Platform. For very complex data architectures or highly specialized needs, established enterprise data warehouses might be the better choice. However, for a vast array of scenarios, Dataverse has a compelling combination of security, scalability, and ease of use.
Avenga is a Gold Microsoft partner
As a Gold Microsoft partner, specializing in application development, application integration, and cloud platform solutions, we deliver Microsoft development and consulting services. Use Power Platform for the advantage of your business: talk to our experts.



 Figure 1.
Figure 1. 









