How to choose the best cloud platform for AI
Explore a strategy that shows you how to choose a cloud platform for your AI goals. Use Avenga’s Cloud Companion to speed up your decision-making.

Java is a powerful language with a variety of frameworks and libraries. That fact makes development in Java relatively easy, but it is also often criticized for the massive amounts of boilerplate code it requires for common tasks.
“Boilerplate code” describes sections of repeatable code that must be included into multiple parts of an application with little or no alteration. The same code can apply from application to application and from project to project. Sometimes reiterating the code just becomes too bulky to handle easily.
Fortunately, Project Lombok came along to help ease this burden. Project Lombok is a library that reduces boilerplate code by utilizing a set of straightforward but powerful annotations.
In order to understand why we may need Project Lombok, let’s assume that we have an entity class, e.g., User, where we want to store ID, name and email. For this requirement, we will need a simple User “Plain Old Java Object” (POJO) that will look like this:
public class User {
private long id;
private String name;
private String email;
public User(long id, String name, String email) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}Usually, we use the auto-generation strategies of our IDE to generate getters, setters, default constructor, hashCode(), equals(), and toString(). However, for simple class implementation with three fields, we would need about 60 lines of code that are not directly contributing anything to our business logic. That type of size increase just makes our code difficult to read or even understand. An inexperienced programmer might think that some valuable logic or algorithm may be hidden somewhere in there.
Furthermore, if in future we would like to change some field name or field type, we would also have to get/set method names and types, modify our constructor(s), and so on.
@Getter
@Setter
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode
@ToString
public class User {
private long id;
private String name;
private String email;
}Project Lombok provides a way to remove the boilerplate code and simplify the development process. This code is fully equivalent to previous one but we don’t worry about common things like getters, setters etc. because Project Lombok will do it on our behalf.
Code above looks nice but somebody can say there are too many annotation. Project Lombok can do it simpler, if you want:
@Data
public class User {
private long id;
private String name;
private String email;
}
That’s only a little part of Project Lombok’s features. Later, we will discuss those annotations in more detail, but for now, let’s see how it works and how to start using it.
Project Lombok does not change source code, but instead generates required code that will be injected directly to the class file (byte-code). This means that all of its “magic” will occur during compilation.

Project Lombok creators figured out that they can use the Annotation Processing phase differently. Annotation processing has been available since Java 5, but a useable API has been available since Java 6 (released in December 2006). The annotation processing API only provides a mechanism to create new source files and process existing ones.
But Project Lombok got around this through non-public APIs, which provide more possibilities than the annotation processing API. Project Lombok hooks into the compilation process as an annotation processor. However, it is not a normal annotation processor, because Project Lombok does not generate new source files, but rather modifies existing ones.
The trick is that Project Lombok modifies the AST, which will have an effect in the generated class file. For example, if a method node is added to the AST, then the class file will contain that new method. By modifying the AST, Project Lombok can do things like generate new methods or inject code into an existing method. The changes made to the AST in the Annotation Processing phase will be visible to the Analyse and Generate phase. Correspondingly, class files will be generated according to the AST that was modified by Project Lombok.
IntelliJ Idea and Eclipse are compatible with Project Lombok. IntelliJ Idea uses the javac compiler by default. Eclipse has implemented its own compiler called Eclipse Compiler for Java (ECJ). Javac and ECJ work with a similar AST structure, but they are implemented very differently. This difference forced Project Lombok creators to write two annotation handlers per annotation: one for javac and one for ECJ. We will consider the installation process separately for IntelliJ Idea and Eclipse.
Lombok does not have direct support for Intellij Idea, but you can install a plugin that adds support for Project Lombok. With this plugin, IntelliJ will recognize all generated code, so you get code completion.
To install lombok plugin in Intellij Idea:
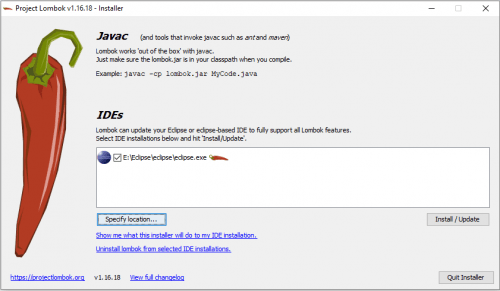
Download and run lombok.jar from the official website. The graphical installer will lead you through the required steps, and will automatically detect all supported IDE’s in your machine:
However, for Intellij Idea and Eclipse projects, you must add lombok.jar in the classpath. For maven, you can simply add the following dependencies in the pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.16.18</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>For Gradle, add the following to your build.gradle file:
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.16.18'
Project Lombok features are divided into two branches: Stable and Experimental. The main difference is that any Experimental feature can be changed or removed in case it is too difficult or is not that significant. Given this, let’s look at the stable features.
These annotations are used for generating getter/setter methods. Annotation can be applied directly for each field, or at the class level. At the class level, getters and setters will be generated for all the non-static fields of your class.
@Getter
public class User {
@Setter private long id;
@Setter private String name;
private String email;
}Generated methods will be public by default but you can specify access modifiers for methods by an AccessLevel, i.e., PRIVATE, PROTECTED, PACKAGE, PUBLIC, or NONE. Annotating a field by AccessLevel.NONE will disable getter/setter generation.
@Getter
public class User {
private long id;
private String name;
@Getter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED) private String email;
}Also, the getter and/or setter method will not be generated if a method with the same name and parameters already exists in your class.
Annotation is used for generating a null-check statement. Annotation can be applied to the parameter of a method/constructor, then a null-check for that parameter will be inserted inside the method or constructor. Also, @NonNull can be used for fields. All the setter methods and constructors generated by Project Lombok will contain a null-check for that field.
public class User {
@Getter @Setter private long id;
@Getter @Setter @NonNull private String name;
@Getter @Setter private String email;
public User(@NonNull long id, String name, String email) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
}The null-check looks like:
if (param == null) throw new NullPointerException("param");Annotations are used to generate an implementation of toString(), equals() and hashCode() methods.
Default implementation of toString() will print the class name and all fields with values separated by commas. Also, you can pass includeFieldNames, which defaults to true, and looks like: fieldName = fieldValue.
Default Project Lombok implementation of toString(), equals() and hashCode() methods contain all non-static fields, but you can customize them by excluding a parameter and generating method(s) only for specified fields. In addition, you can add the setting callSuper, in this case Project Lombok, which will include the appropriate methods of your superclass in the generated methods.
For example, hashCode(), the result of super.hashCode(), is included in the hash algorithm, and for equals(). The generated method will return false if the super implementation thinks it is not equal to the passed in object.
@ToString(of = {"name", "email"})
@EqualsAndHashCode(exclude = "id")
public class User {
private long id;
private String name;
private String email;
}Annotations are used for constructor generation. NoArgsConstructor is used to generate constructor without parameters, but if that is impossible, e.g., class contains final variables which must be initialized, etc., compiler will generate an error. In this case annotation should be used with parameter:
@NoArgsConstructor(force=true).
Then all final fields are initialized with default values for type.
@NoArgsConstructor(force = true)
public class User {
private long id;
private String name;
private String email;
}
@AllArgsConstructor is used to generate constructor for each field in a class. Also, for fields marked with @NonNull, annotation null-check will be generated.
@RequiredArgsConstructor will generate constructor for each field that requires specific handling. Constructor will be generated for all non-initialized final fields and fields marked as @NonNull.
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class User {
private final long id;
@NonNull private String name;
private String email;
}Also, constructor annotations can be used with parameters access and staticName. access specifies an access level similar to @Getter/@Setter. staticName generates a private constructor for class and static factory method as a wrapper for private constructor.
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class User {
private final long id;
@NonNull private String name;
private String email;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = User.of(1, "example");
}@Data is a pack of annotations that bundles the features of @ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode, @Getter/@Setter and@RequiredArgsConstructor. In other words, @Data generates all boilerplate normally associated with simple POJOs.
However, the parameters of these annotations, such as callSuper, includeFieldNames and exclude, cannot be set with @Data. If you need to set non-default values for any of these parameters, just add those annotations explicitly. To reduce the boilerplate when constructing objects for classes with generics, you can use the staticConstructor parameter to generate a private constructor, as well as a static method that returns a new instance, similar to staticName for constructors.
@Value is the immutable version of @Data. The main difference is that the class and all fields are made final by default and setters are not generated. Also, the staticConstructor parameter is supported by @Value annotation.
Annotation can be applied to resources, e.g., (InputStream, OutputStream, etc., and used to guarantee that resource will automatically clear itself before it goes beyond the scope of visibility. At the end of the scope, method close() is called.
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
@Cleanup InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
@Cleanup BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String line = "";
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
}If the resource does not provide a close() method, but offers some other no-argument method, you can specify the name of this method like so: @Cleanup(“dispose”).
@Log produces and includes in class the private static final log field, initialized to the name of class. Project Lombok supports the following loggers:
| Annotation | Logger |
| @CommonsLog | org.apache.commons.logging.Log |
| @JBossLog | org.jboss.logging.Logger |
| @Log | java.util.logging.Logger |
| @Log4j | org.apache.log4j.Logger |
| @Log4j2 | org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger |
| @Slf4j | org.slf4j.Logger |
| @XSlf4j | org.slf4j.ext.XLogger |
@Synchronized is a safer version of the synchronized method modifier. It is safer because a synchronized modifier locks on the class instance, but Project Lombok implementation locks on generated objects. Annotation can be used on static and instance methods, as well as passing the name of an existent object to lock like this:
public class SynchronizedExample {
private final Object readLock = new Object();
@Synchronized
public static void hello() {
System.out.println("world");
}
@Synchronized
public int answerToLife() {
return 42;
}
@Synchronized("readLock")
public void foo() {
System.out.println("bar");
}
}@SneakyThrows can be used for methods in order to throw checked exceptions as unchecked. It is merely a trick with compiler. In the bytecode, all exceptions, checked or unchecked, can be thrown without restrictions. Project Lombok creators recommend use of this annotation in the following situations:
String(someByteArray, “UTF-8”), which declares that it throws UnsupportedEncodingException even though UTF-8 is guaranteed by the Java spec to always be present.Runnable.run(), which does not throw any checked exceptions.public class Example implements Runnable {
@SneakyThrows(UnsupportedEncodingException.class)
public String bytesToString(byte[] bytes) {
return new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
}
@SneakyThrows
public void run() {
throw new Throwable();
}
}The problem with @SneakyThrows is that the Java compiler does not allow you to catch sneakily thrown checked exceptions. So, let this serve as a warning that you should not utilize the @SneakyThrows mechanism without thinking through its use.
Project Lombok implements a very powerful @Builder feature that allows the use of a Builder Pattern to create new instances.
@Builder
public class CoreCampForm {
private String name;
private String company;
private String mobilePhone;
private String skype;
private String email;
}Now we are able to create new users fluently like this:
public static void main(String[] technologies) {
CoreCampForm.CoreCampFormBuilder builder = CoreCampForm.builder()
.name("Mykhailo")
.company("CoreValue")
.mobilePhone("Xiaomi")
.skype("Echo/Sound Test Service");
//CoreCampForm.CoreCampFormBuilder(name=Mykhailo,
// company=CoreValue, mobilePhone=Xiaomi,
// skype=Echo/Sound Test Service,
// email=null}
}By annotating constructor or method, a nested builder class will be generated for all parameters of annotated constructor or method, respectively. For constructor, the builder class will be named the same as for class but for method “ReturnType” + “Builder”. Both cases will be generated internally toString() method for builder parameters.
Along with @Builder you can use @Singular for parameters, when annotating constructor or method, or fields when annotating class. @Singular can only be applied to collection types. For fields/parameters marked by @Singular two methods will be generated for initializing. One method adds a single element to the collection, and the other adds all elements of a passed collection to the collection. In addition, clear method will be generated for collection.
Let’s modify the example above and provide possibility to create form with a few technologies:
Annotation can be applied to class, constructor or method. In the case of annotating class, the result will be a generated, nested builder class for all non-static fields. The builder class will be named “Classname” + “Builder” and will contain implementation of the toString() method.
By annotating constructor or method, a nested builder class will be generated for all parameters of annotated constructor or method, respectively. For constructor, the builder class will be named the same as for class but for method “ReturnType” + “Builder”. Both cases will be generated internally toString() method for builder parameters.
Along with @Builder you can use @Singular for parameters, when annotating constructor or method, or fields when annotating class. @Singular can only be applied to collection types. For fields/parameters marked by @Singular two methods will be generated for initializing. One method adds a single element to the collection, and the other adds all elements of a passed collection to the collection. In addition, clear method will be generated for collection.
Let’s modify the example above and provide possibility to create form with a few technologies:
@Builder
public class CoreCampForm {
private String name;
private String company;
private String mobilePhone;
private String skype;
private String email;
@Singular private List<String> technologies;
}
And now we are able to initialize form as follows:
public static void main(String[] technologies) {
CoreCampForm.CoreCampFormBuilder builder = CoreCampForm.builder()
.name("Mykhailo")
.company("CoreValue")
.mobilePhone("Xiaomi")
.skype("Echo/Sound Test Service");
builder.technologies(Arrays.asList(technologies));
builder.clearTechnologies();
builder.technology("Java");
builder.technology(".Net");
System.out.println(builder.toString());
//CoreCampForm.CoreCampFormBuilder(name=Mykhailo,
// company=CoreValue, mobilePhone=Xiaomi,
// skype=Echo/Sound Test Service,
// email=null,technologies=[Java, .Net])}
}
Project Lombok creators described this feature as: “Sup dawg, we heard you like annotations, so we put annotations in your annotations so you can annotate while you’re annotating.”
So, as you could guess, this feature provides the ability to add annotation to generated code. You can include annotations to parameters, methods and constructors, but for now this feature is experimental.
onMethod option allows for the addition of annotation on generated method, supported by @Getter and @Setter.
onConstructor option allows for the addition of annotation on generated constructor, supported by @NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor, @AllArgsConstructor.
onParam option allows for the addition of annotation to parameter, supported by @Setteronly.
@AllArgsConstructor(onConstructor=@__(@JsonCreator))
public class OnXExample {
@Getter(onMethod=@__({@Id, @Column(name="unique-id")}))
@Setter(onParam=@__(@Max(10000)))
private long id;
}Delombok is a part of Project Lombok that offers a possibility to transform source java code into java code containing all of Lombok’s transformations. The idea of creating this tool is that not all tools are covered by Project Lombok, e.g., Google Web Toolkit, Javadoc, etc., and sometimes you simply cannot use Project Lombok. Delombok can be used in this case in order to generate the corresponding source code that you can use without any remaining dependencies on Project Lombok. Delombok is a great instrument that helps you to check generated code and decide whether to use some features.
To generate code by Delombok you need to call delombok command provided by lombok.jar. It will look like this:
java -jar lombok.jar delombok src -d src-delomboked
java -jar lombok.jar delombok -f pretty src -d src-delomboked
java -jar lombok.jar delombok –format-help
Also, for a maven project, you can use lombok plugin:
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.16.16.0</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>delombok</id>
<phase>generate-sources</phase>
<goals>
<goal>delombok</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<addOutputDirectory>false</addOutputDirectory>
<sourceDirectory>src/main/java</sourceDirectory>
</configuration>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>test-delombok</id>
<phase>generate-test-sources</phase>
<goals>
<goal>testDelombok</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<addOutputDirectory>false</addOutputDirectory>
<sourceDirectory>src/main/java</sourceDirectory>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>As we have shown, Project Lombok is a great tool and can significantly facilitate the development process. In particular, this benefit will be noticeable at the start of the project, because you can focus on business logic and without worrying about common things. If you are still in doubt whether to use it or not, note that Spring has been using Project Lombok for a long time, e.g., Spring Data, Spring HATEOAS, etc.
Of course, Project Lombok is not the only one boilerplate buster framework in Java world. Immutables or Google Auto Value allow you to enrich or modify code during compilation providing similar usage of annotation processors. Byte Buddy or Javassist provide similar features for “bytecode enhancing,” but their approach is different. All their magic happens at runtime. Implementation of the builder pattern makes Immutables looks interesting, but Project Lombok has a larger variety of features.
In conclusion, here are some recommendations for using Project Lombok based on my experience:
So, don’t be afraid to use Project Lombok. You will soon find it irreplaceable for development.
* US and Canada, exceptions apply
Ready to innovate your business?
We are! Let’s kick-off our journey to success!