Biopharma trends 2024, midyear update: what is relevant as of June-July 2024
Discover the latest trends in biopharma for 2024, including AI-driven drug discovery, personalized medicine, and other technologies transforming the industry.

There are more than a few ways to leverage mobile in healthcare and biotech to enhance positive outcomes both for patients and medical professionals.
The proliferation of mobile technology in healthcare has been remarkable in recent years. In many aspects, mHealth apps have revolutionized medical and pharmaceutical practices across a broad spectrum. With their help, care providers are now achieving better patient outcomes in areas ranging from condition monitoring, general wellness, and cardiology to weight management, disease management, and evaluation. And, this is clearly contributing to the overall digital health market growth. According to the latest estimates, its size was valued at $211 billion in 2022 and it is projected to grow to USD 780.05 billion by 2030. Notably, mHealth is the second-largest segment after telemedicine, as depicted in Figure 1.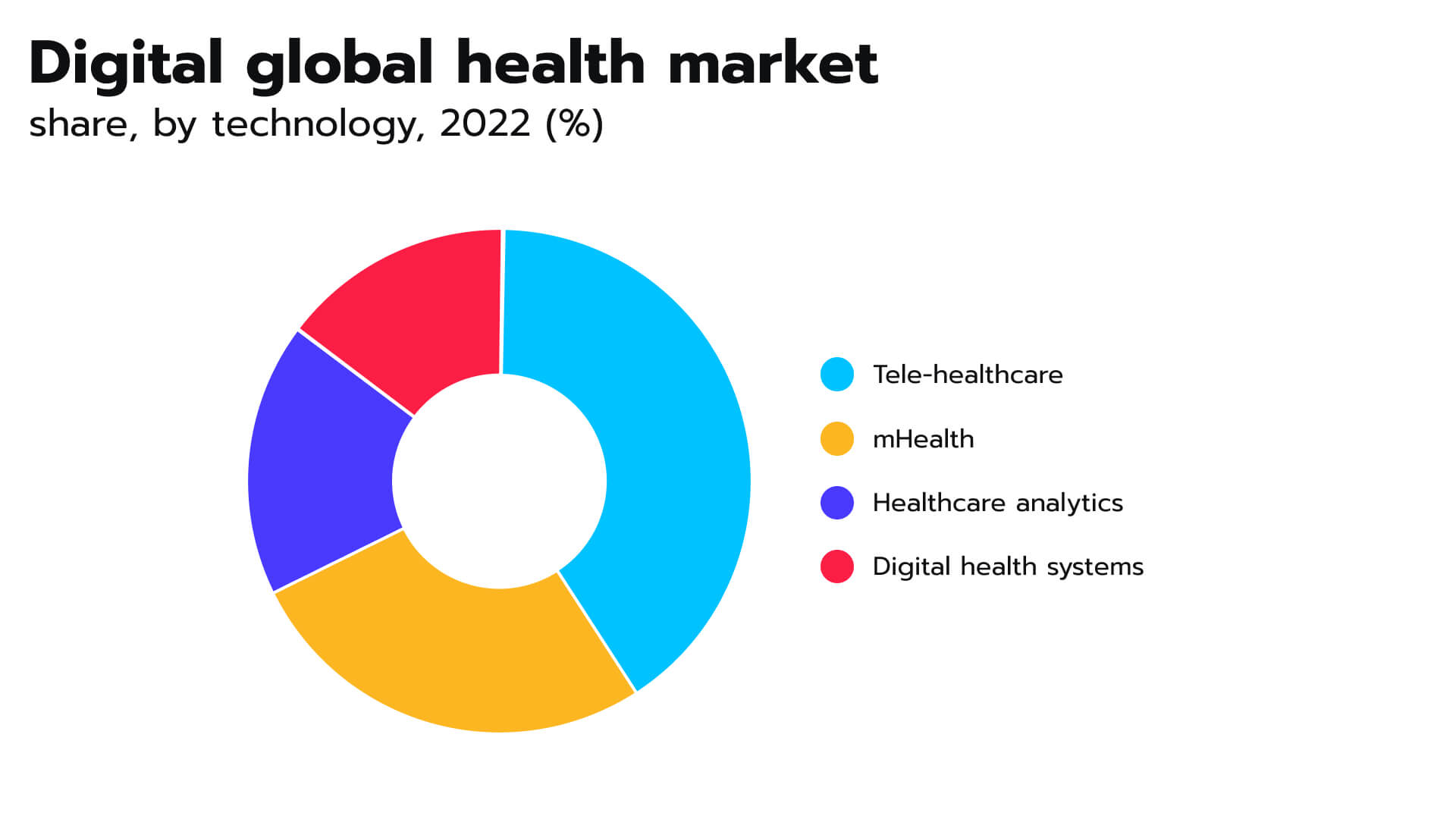 Figure 1. Global digital health market
Figure 1. Global digital health market
While initially mHealth mostly revolved around recording patient data, now it increasingly employs analytics, medical IoT, and Machine Learning-based features. These changes have far-reaching implications for healthcare and biotech organizations as well as patients. They are able to facilitate a shift from reactive to preventive care in addition to empowering companies to provide unparalleled levels of service personalization. What’s more, they can profoundly improve the accessibility of medical care, particularly to underserved communities.
Studies have repeatedly shown that mobile technology in healthcare improves care quality and reduces operational costs for care providers. The apps’ ability to eliminate logistical barriers also allows innovative healthcare and biotech players to offer diverse services to patients, regardless of their location or connection to the established healthcare system.
For medical companies and physicians, software platforms are powerful for elevating patient medication adherence. Their automated prescription and refill reminder features plus educational content can motivate patients to follow treatment plans and adopt healthier lifestyles. Also, the ease of collecting and transmitting patient data to healthcare providers, which platforms offer, facilitates comprehensive in-between visit patient monitoring.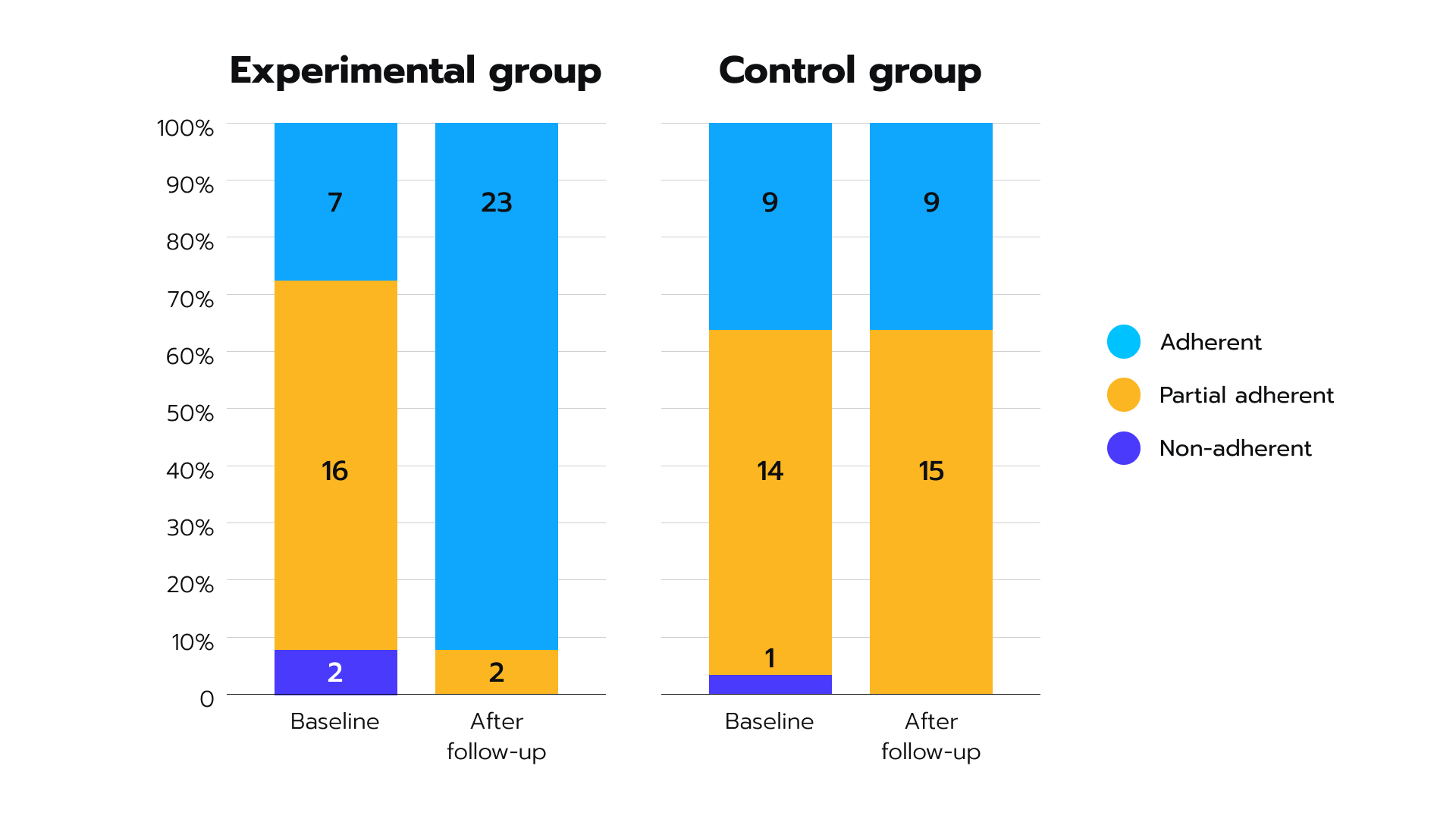 Figure 2. Treatment adherence in groups using mobile (experimental) and conventional (control) monitoring
Figure 2. Treatment adherence in groups using mobile (experimental) and conventional (control) monitoring
The latest digital health apps, which increasingly incorporate data from wearables and use Machine Learning algorithms to analyze trends, significantly simplify patient monitoring. They pick up deviations from a patient’s health status even quicker than a physician could and alert healthcare providers immediately, allowing for faster interventions and better results.
Learn more about how we enhanced customer experience to increase conversion rates for Klara. Success story
For individuals who take multiple medications at varying dosages at once (and often struggle to remember the names of each drug), mHealth apps can act as electronic journals that healthcare professionals can refer to when admitting such patients. With access to information about previous prescriptions, as well as a complete history of refills, pickups, and dosage changes, clinicians can avoid prescribing medication that may interact negatively with other drugs or cause an individual to have an allergic reaction.
The advantages of mobile in healthcare don’t end there. The applications can also maintain a record of the clinics a patient has visited, the treatments they received, and the names of their previous clinicians. As a result, they support seamless care transitions across different settings and enhance coordination among care providers.
One of the major pros of launching an app for a biotech company is that it can drastically increase the company’s reach. And if provided as an additional service, the app can contribute to the success of patients’ medical outcomes by enabling easier adherence, thorough monitoring, etc. Combined, these factors can help put a pharma brand’s name on the map and build positive perceptions among patients and healthcare professionals. And this in turn, opens the path to competitive differentiation and customer loyalty.
Just like apps enable close monitoring on the physicians’ side, they can be used by biotech organizations to gather information on how their medicines are being used, collect feedback, and determine the overall level of satisfaction with their products. These kinds of comprehensive insights into clients’ usage habits and behaviors can then help pharmaceutical providers find ways to improve their medicines and build effective marketing strategies.
Special attention should also be paid to how mobile applications have been used in pharmaceutical testing. While the traditional in-person trials remain the main source of clinical knowledge (and thus, they’re still the primary driver for healthcare advancement), they usually take years to finish (Figure 3.) Besides that, there are specific challenges to in-person trials, including the frequent inability of researchers to recruit a sufficient number of varied cohorts in a timely manner and monitor the day-to-day fluctuations of patients’ disease severity. Oftentimes, these changes go completely undetected during episodic evaluations. Apps can help biotech companies collect real-world evidence faster and accumulate more data on their medicine’s short-term and long-term effects. Additionally, the firms get to observe different disease trajectories in various groups of people at a fraction of the cost of a conventional study.
Multiple large-scale clinical studies involving mobile technologies have already been conducted in the US and across the globe. And, unsurprisingly, they had a huge reach because the participants could apply, learn details, and consent to the procedure specifics without ever having to set foot in a lab.
Another notable benefit of mobile pharma apps is the enhanced monitoring capabilities researchers get from them. The apps can access deeper insights into people’s day-to-day experiences of the disease and get trial data that is free of bias, which is rarely the case when scientists ask patients to recall their health status throughout the trials’ days, weeks, or months.
While the benefits of launching a mobile healthcare app are manifold, its success and efficacy will depend upon the features it possesses. Not only should an application provide convenience to the user, but it should also help them tackle significant issues.
Below, we provide some examples of popular healthcare and biotech apps that you can draw inspiration from when deciding on your own market entry. Some of them are targeted more towards clinicians, some cater solely to end-clients, and others fall in between. Ultimately, all of these apps can significantly contribute to establishing and promoting your brand name, as well as winning or increasing customer loyalty.
Pharmaceutical applications of this type usually provide a reliable source of medical information, including lists of diagnoses, symptoms of various diseases, responses to frequently asked medical questions, accessible drug comparisons, and other treatment-related information.
They serve as a convenient decision support tool for clinicians, helping them stay informed about the properties of the latest drugs available on the market and as a trusted source of patient disease management information.
These apps simplify medication management by ridding patients of the need to stand in line at pharmacies, sort pills at home, and repeatedly refill prescriptions. They can also aid in handling therapy changes and streamline communication between individuals and insurance companies regarding medication purchasing. These issues are critical, especially for seniors and those taking multiple drugs simultaneously. Hence, companies that offer medicine management apps with an intuitive user interface, automatic order requesting features, simplified copay management, and timely warnings of potential drug interactions have the potential to gain brand recognition and customer loyalty quickly.
Learn more about how we designed an innovative drug ordering system form QPharma. Success story
To attract and retain users both among patients and clinicians, an app must optimize the complex workflow of ordering and managing multiple pills. Its advanced features, such as automatic checking for prior authorizations and other potential formulary issues before the dispense date, can provide added value and make the provider company stand out from competitors. Overall, drug management tools empower patients to take control of their end-to-end medication management and prevent issues that arise from medication mismanagement.
While these apps can somewhat resemble the general reference applications we’ve already discussed, they boast far more specialized functionality. Essentially, they are designed to help pharmacists, as well as RNs, physicians, paramedics and other healthcare professionals, be more effective during their shifts.
To do so, they typically contain a frequently updated drug monograph library with drug IDs, information about correct dosings, side effects, medicine interactions, etc. Also, the feature that is equally as crucial – and one healthcare professionals use daily – is a clinical calculator.
These tools enable physicians to determine the correct renal dose adjustments (both for pediatrics and adults), ideal and adjusted body weights, acetominatec toxicity (for which the Rumack-Matthew monogram should also be incorporated into the platform), peripheral IV fluids (if we’re talking about osmolality calculators), and much more. They help provide faultless service even in complicated or emergency situations.
Another important feature is a timer, which helps to administer drugs at precise intervals, and an emergency-specific database including:
These applications ensure all the necessary data a medical professional might need is always at their fingertips and that they are free from having to do time-consuming calculations; the app can rapidly compute all the dosages and provide necessary suggestions.
Whether delivered as one sophisticated mobile pharma app with a wide range of features or a suite of tools, this functionality can drastically reduce the risk of medical error and enable healthcare professionals to provide better care. Thus, a branded platform of this kind allows pharma firms to establish themselves as reliable, knowledgeable, and helpful providers of tools, drugs, and services in the medical industry, win healthcare professionals’ trust, and, of course, bring in new sources of revenue.
Regardless of the specific mHealth application being developed and the type of healthcare or pharmaceutical organization involved, there are some general guidelines that can enhance the application’s overall performance.
At the most basic level, any mHealth or Pharma app must enable the digitization of people’s healthcare and wellness needs while also using data to provide personalized experiences. If these two principles are upheld, an app will drive loyalty and, ultimately, become a huge competitive differentiation factor.
To be successful, the app should feature an intuitive interface that ensures a user-friendly mobile experience akin to popular apps in the banking, hospitality, retail, and e-commerce sectors. Additionally, implementing robust security measures is critical as well, and the main focus here should be on fortifying the app against cyber threats while effectively managing the intricacies associated with handling protected health information.
As far as more sophisticated suggestions go, the development of effective mHealth applications requires a nuanced preliminary analysis approach that involves conducting demographic studies. This involves executing comprehensive preliminary research and analyzing potential target users in terms of age, gender, income, and other demographics. This data can point to the audience’s technological preferences and help organizations tailor their solutions to their specific needs. For maximum impact, mHealth platforms should be designed to be accessible via various communication channels and platforms.
Infrastructure and local network research are also crucial to the success of mHealth applications. For example, if the platform aims to improve care in underserved rural areas, potential broadband limitations should be taken into account. Similarly, if an app is designed to benefit small-practice physicians, it is important to note that they are often the most affected by broadband gaps, which can render them incapable of realizing the full potential of the app’s functionality. Furthermore, detailed plans should be in place to handle continuity problems and data loss, which could also arise due to poor local networking infrastructure.
Innovation in payments has always been a challenge for mHealth because it’s hard to accommodate reimbursements for chronic disease management and various scopes of mobile services. To address these challenges, sophisticated self-service portals containing financial, clinical, and seamless mobile payments should be devised and integrated into the app. Additionally, advanced security mechanisms must be devised, as mHealth and Pharma applications, including those that act as medical devices or collect patients’ data, are subject to heavy regulatory scrutiny.
Finally, when engineering certain ‘treatment-helper’ systems, it is essential to assess disease dynamics. mHealth functionality can support various aspects of wellness, fitness, care provision, and disease management, but only if the approach is well-suited to the specific condition. Some medical goals lend themselves better to mHealth than others and careful consideration of disease dynamics is necessary to ensure high-impact outcomes.
As healthcare organizations and biotech companies strive to provide greater value to patients and caregivers, the development of mHealth apps and digital support programs has gained significant momentum. In this article, we have explored how well-designed medical software can simplify the daily health management needs for healthcare professionals and patients alike, as well as outlined the tangible benefits that an app launch can bring to an organization.
Furthermore, we have delved into the crucial considerations healthcare organizations must contemplate when launching a mHealth app, including conducting different types of thorough target user research. If you’d like to learn more about the benefits of utilizing mobile technology in healthcare and optimizing mHealth apps’ efficiency, contact our experts for a free consultation.
* US and Canada, exceptions apply
Ready to innovate your business?
We are! Let’s kick-off our journey to success!